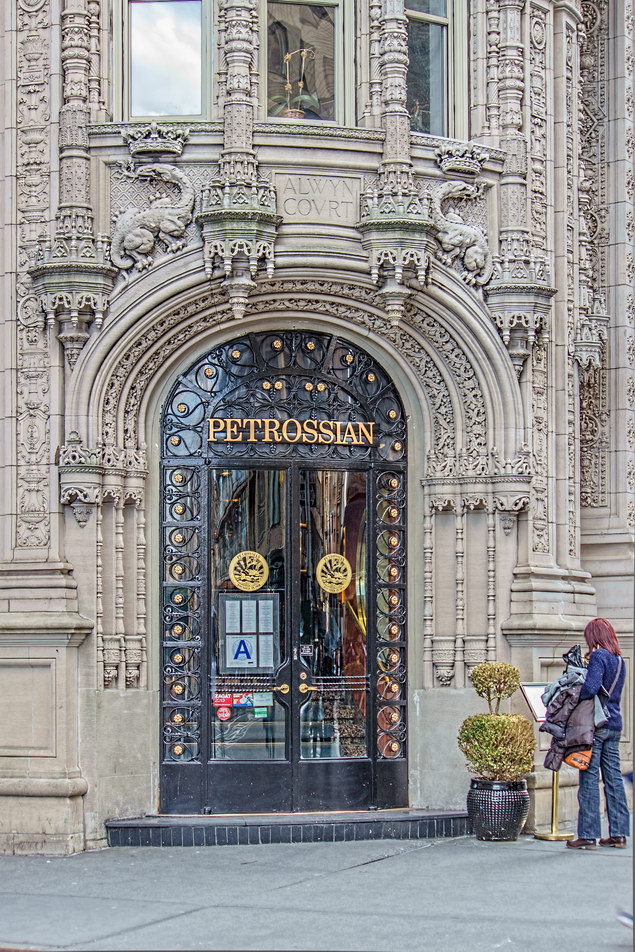
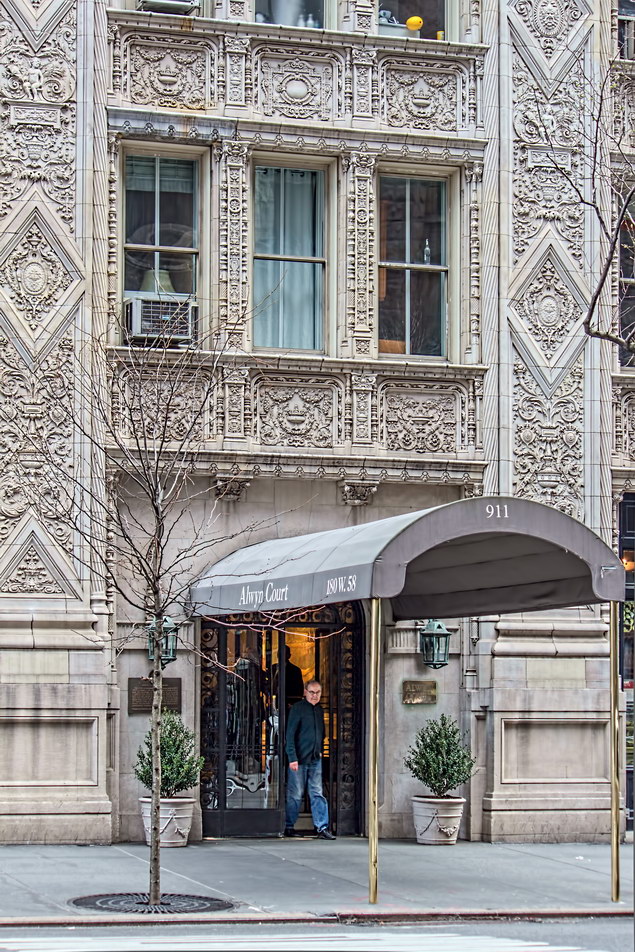
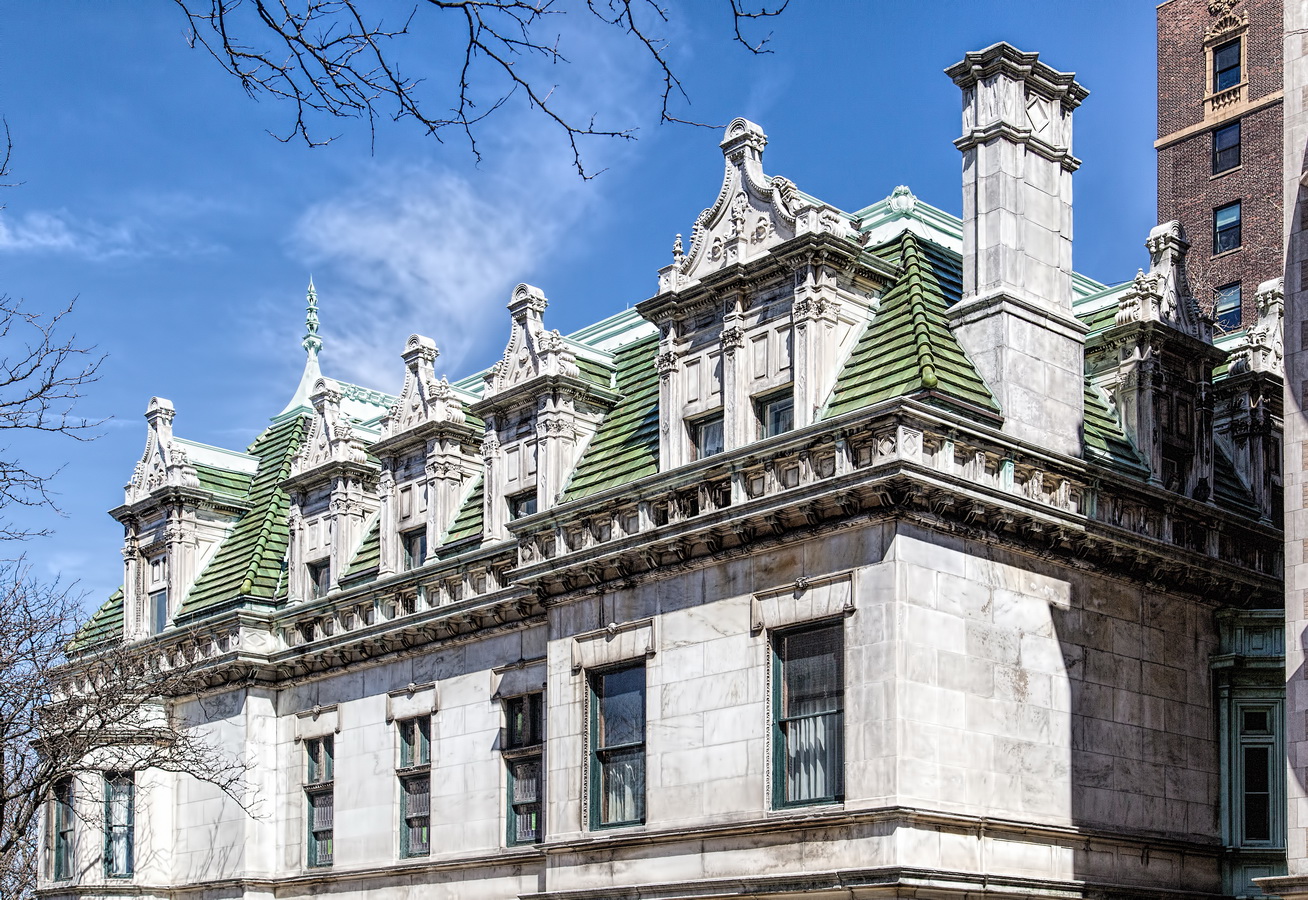
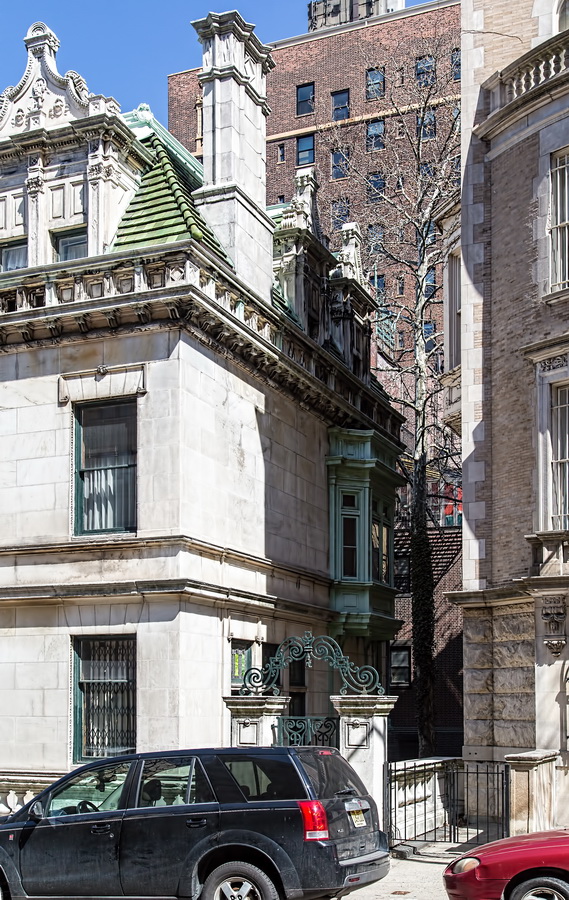
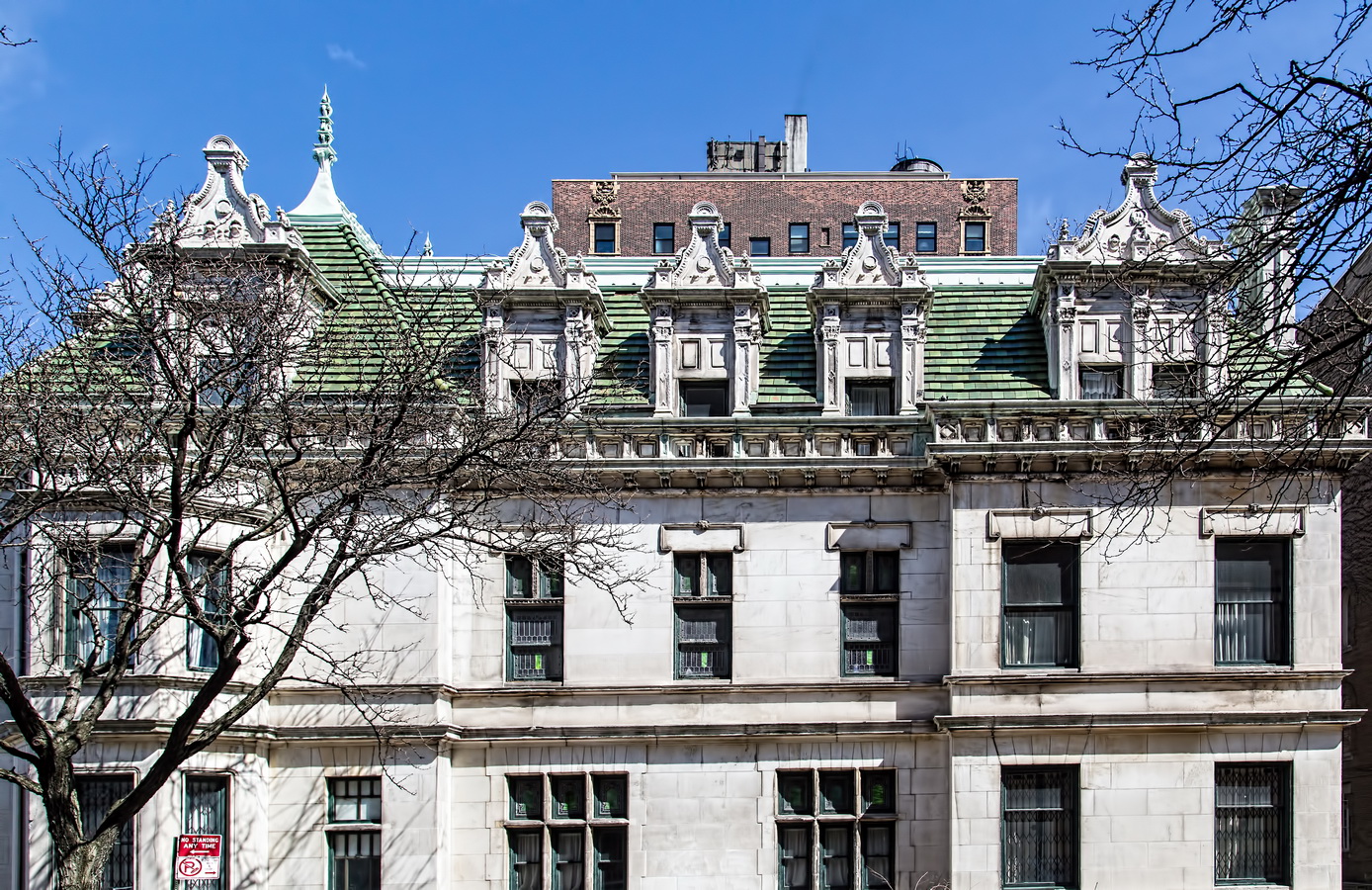
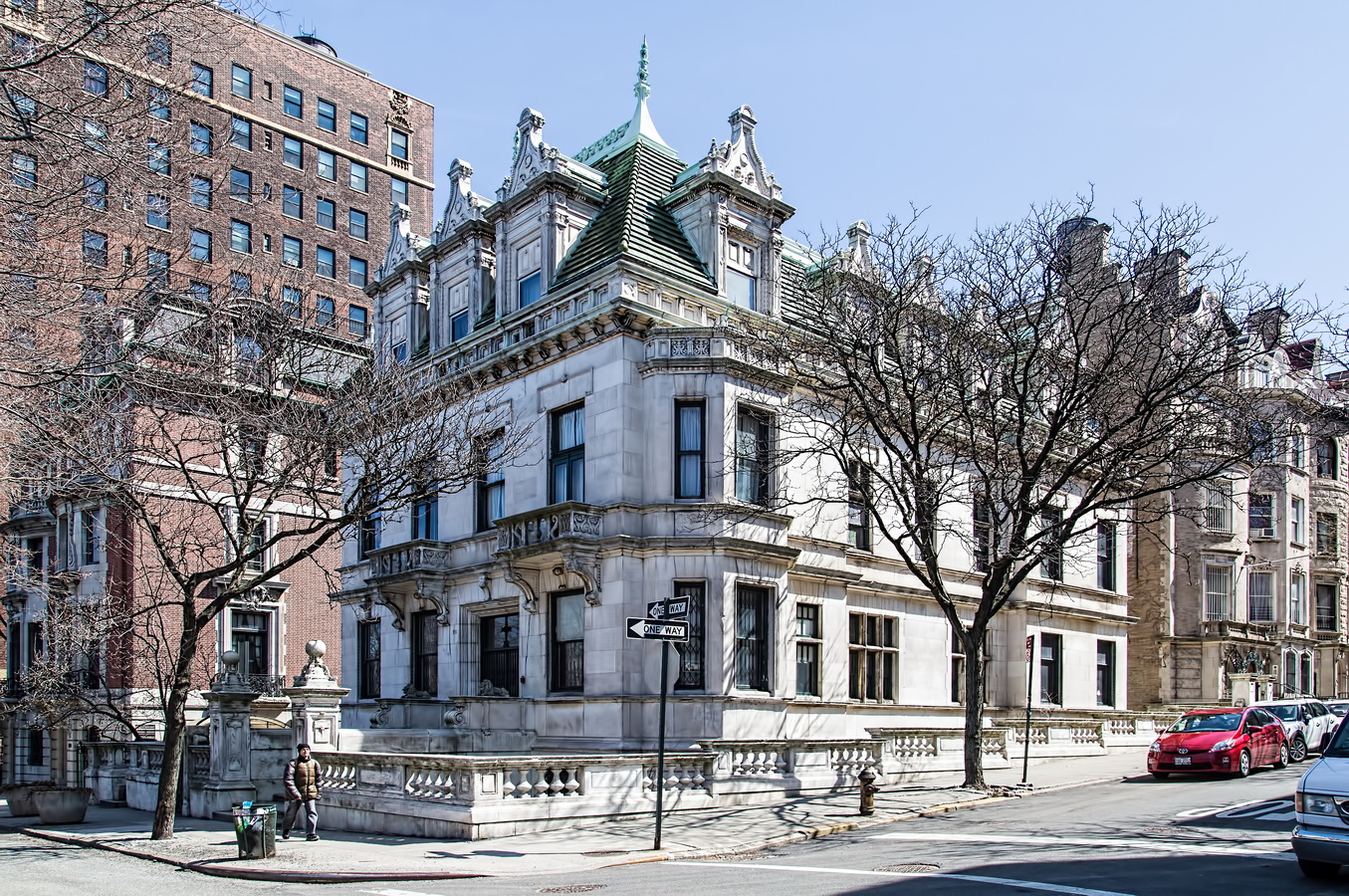
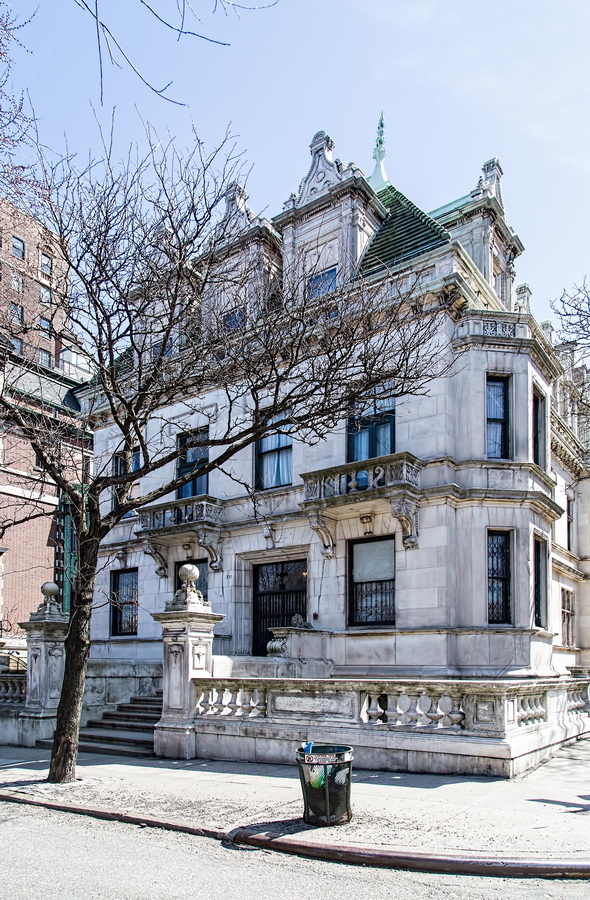
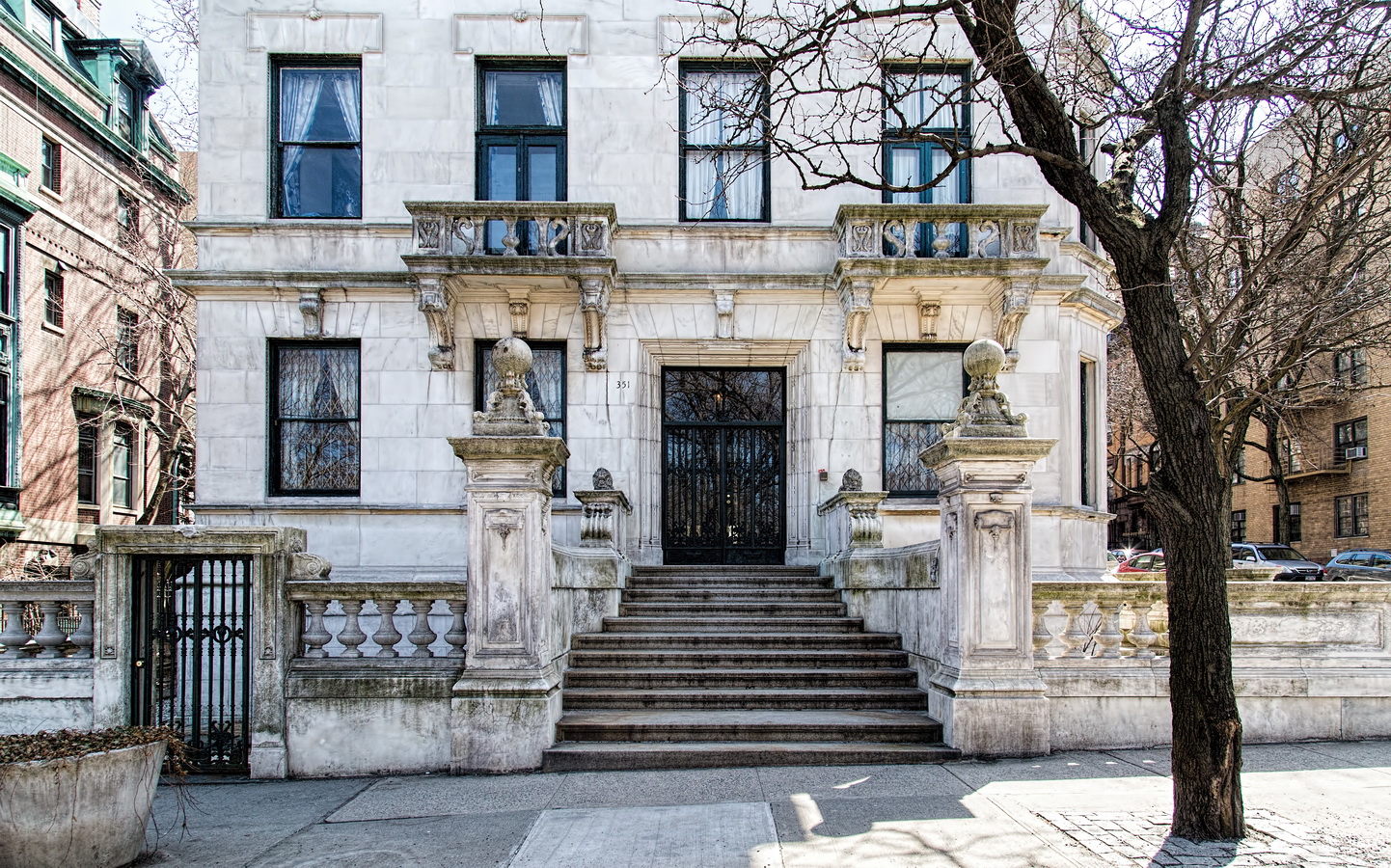
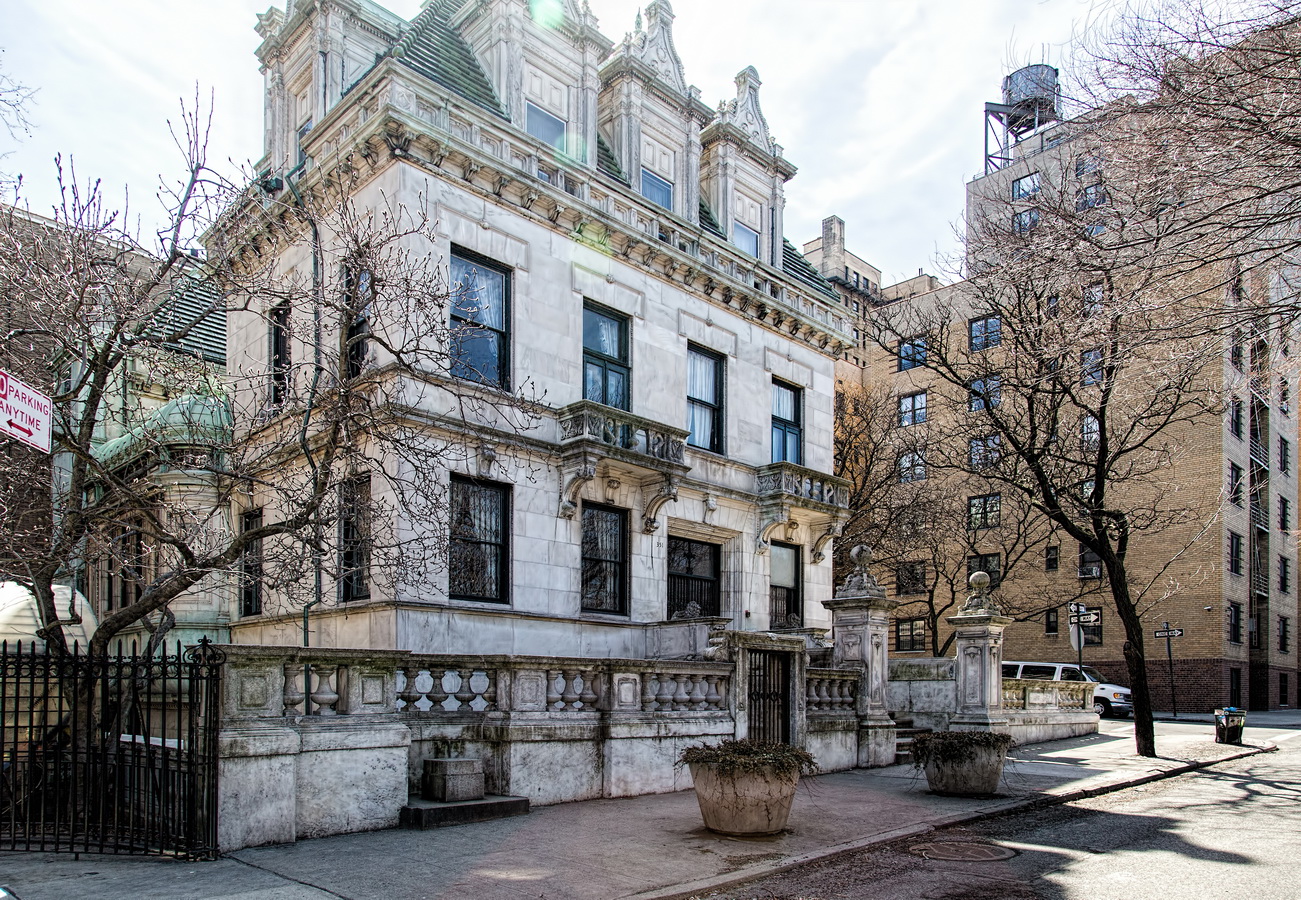
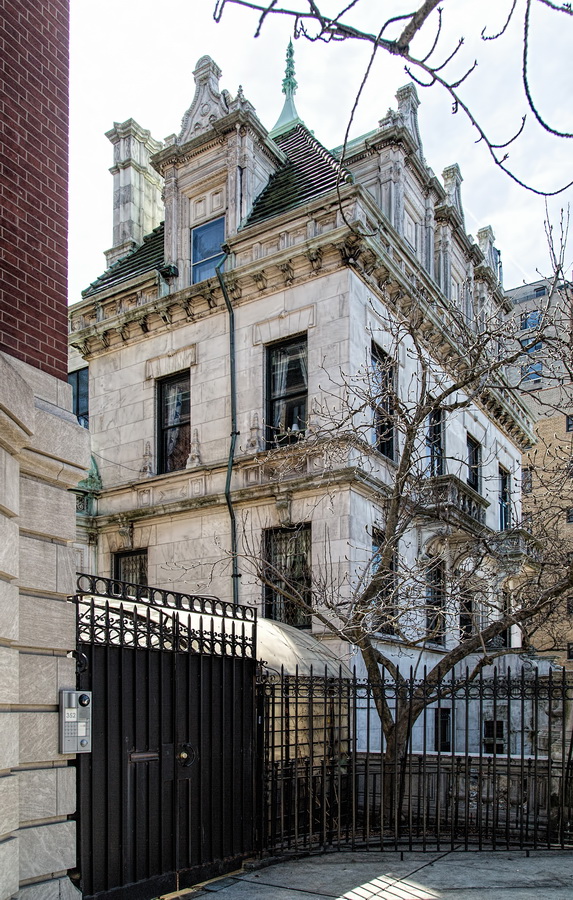
The Sherry Netherland must be bored by now with all of the superlatives lavished upon it. But if actions speak louder than words, consider this: a Sherry Netherland 18th floor apartment recently went on the market (September 2012) for $95 million. (To tell the whole truth, that’s the entire 18th floor – 7,000 square feet plus 2,000 square feet of terrace – seven bedrooms/seven baths – but still: $95 million!)
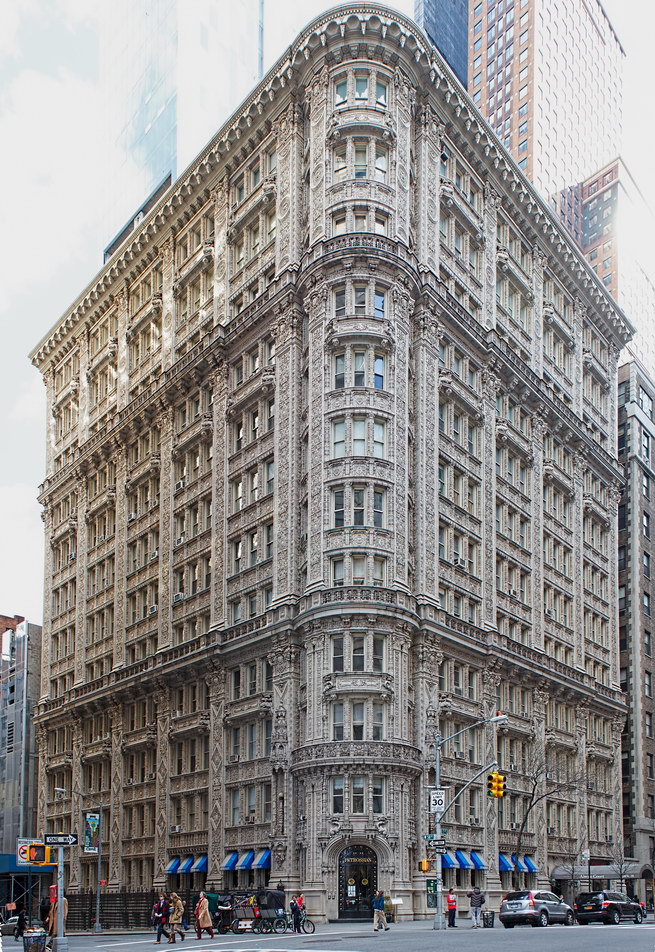
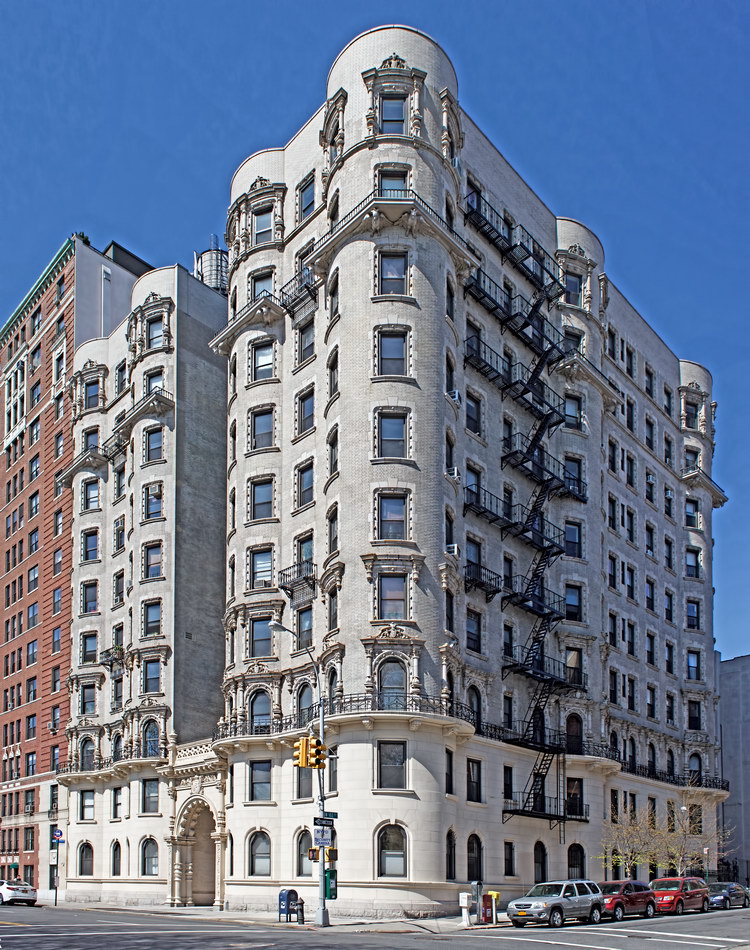
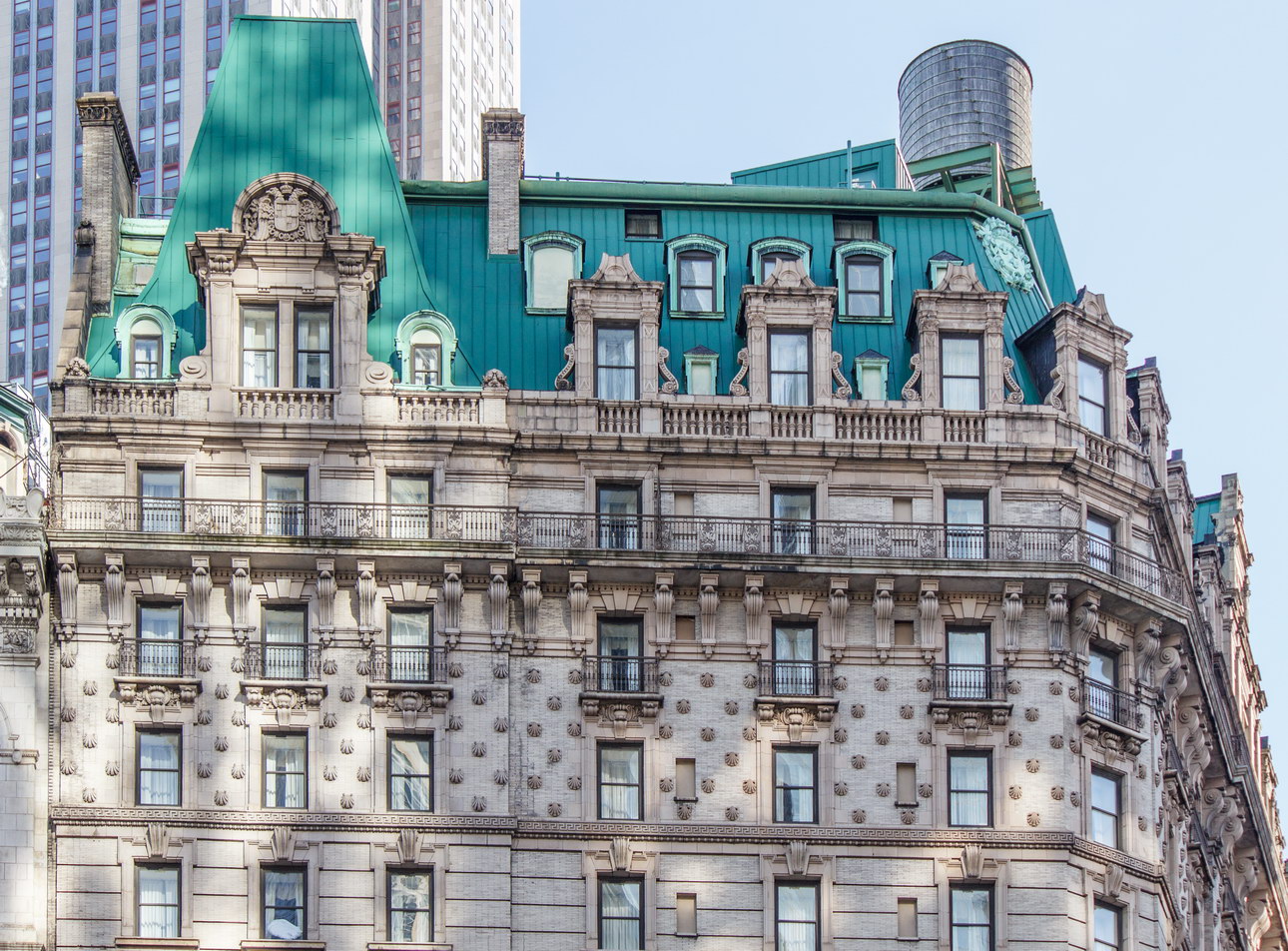
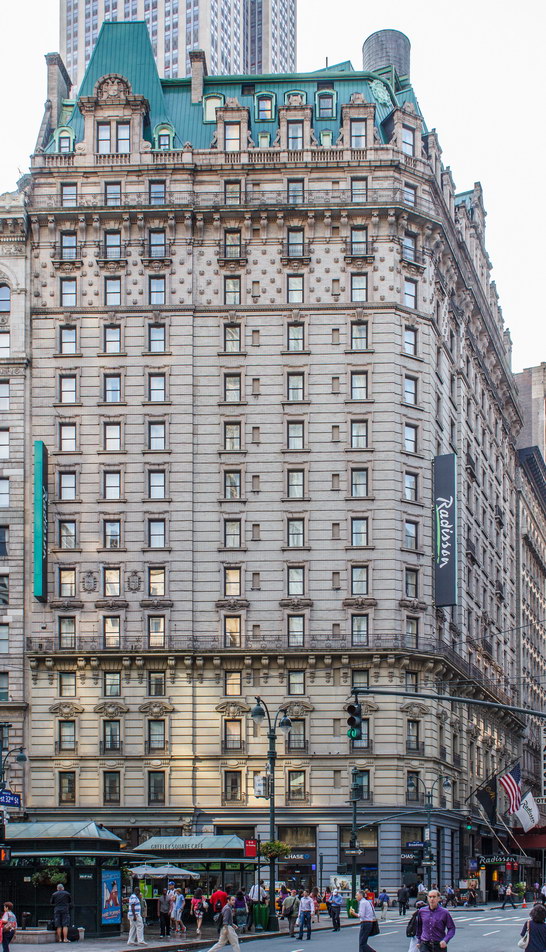
The Sherry Netherland is not, oddly enough, a New York City landmark unto itself (although the clock in front of the hotel is – go figure); it is part of the Upper East Side Historic District, along with the Hotel Pierre, Metropolitan Club, and other classics. The 40-story building was the tallest apartment-hotel in New York when built, in 1927.
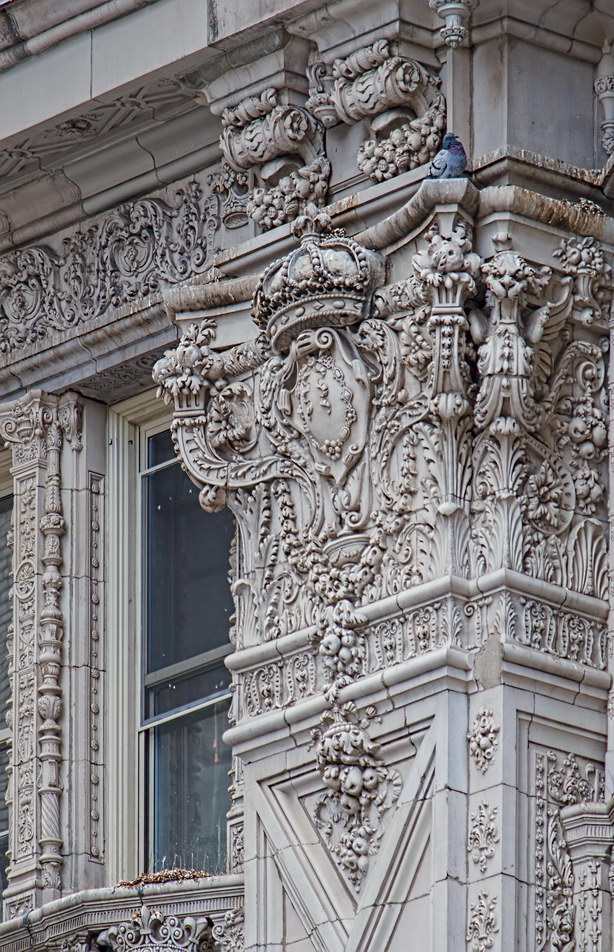
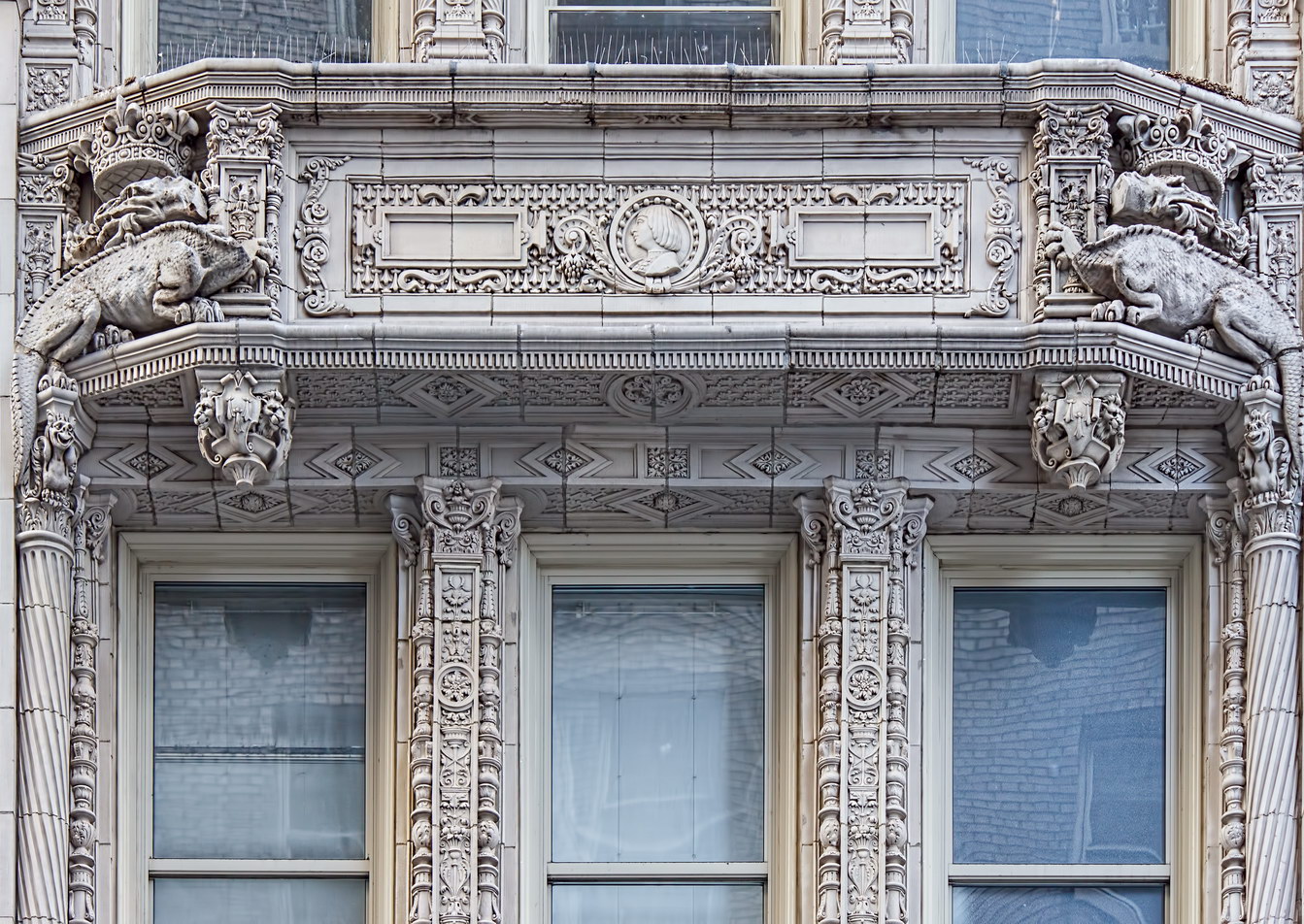
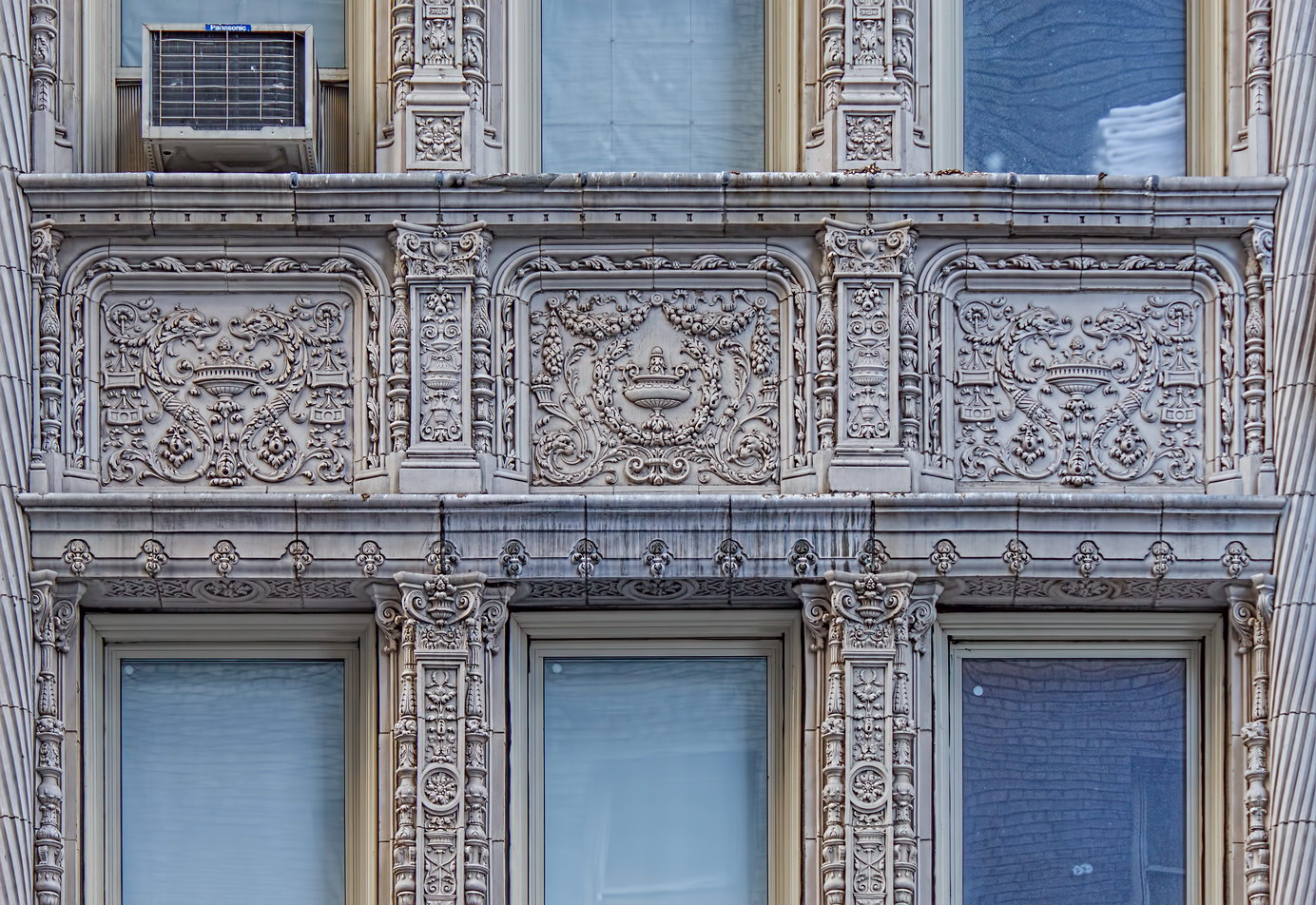
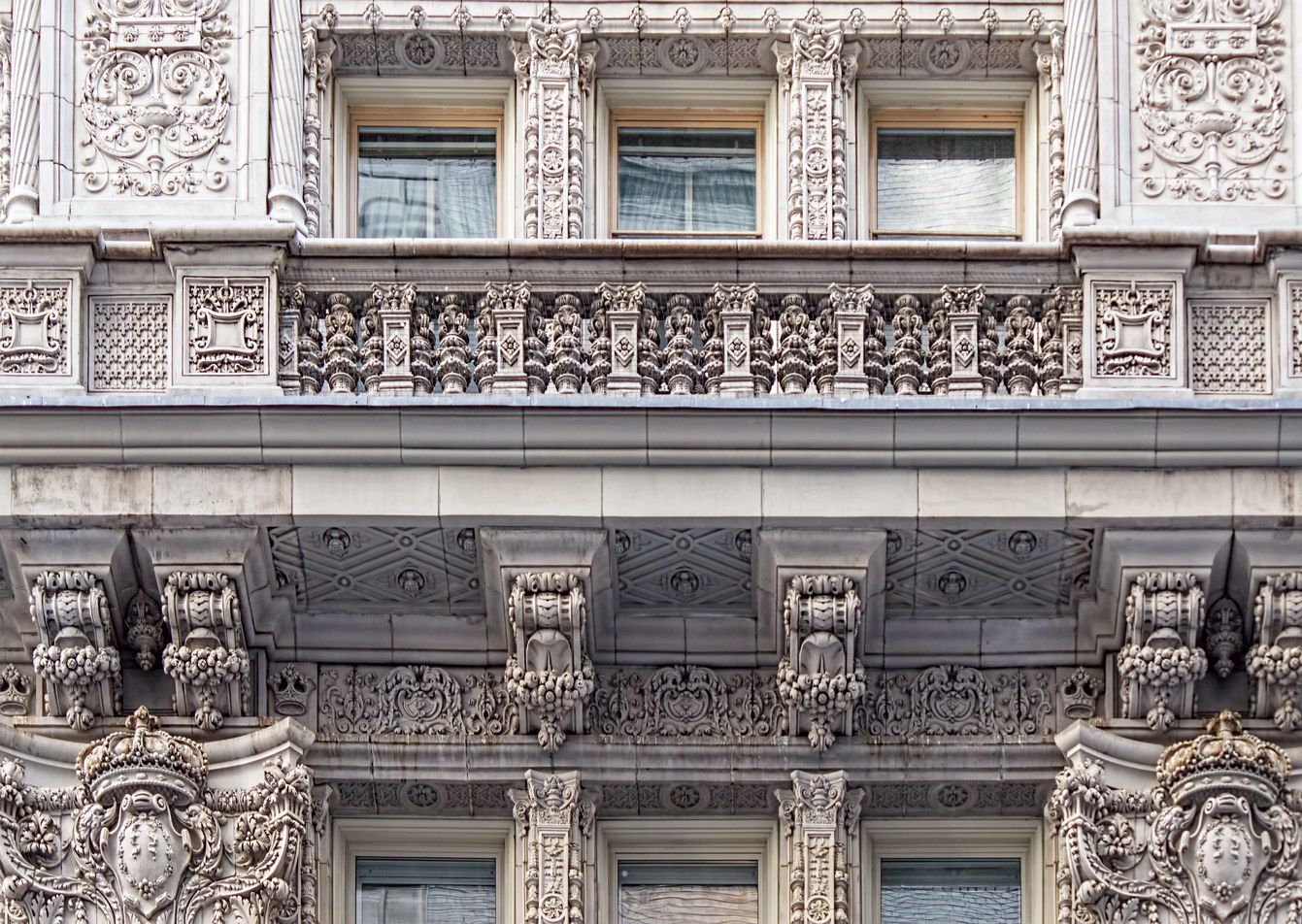
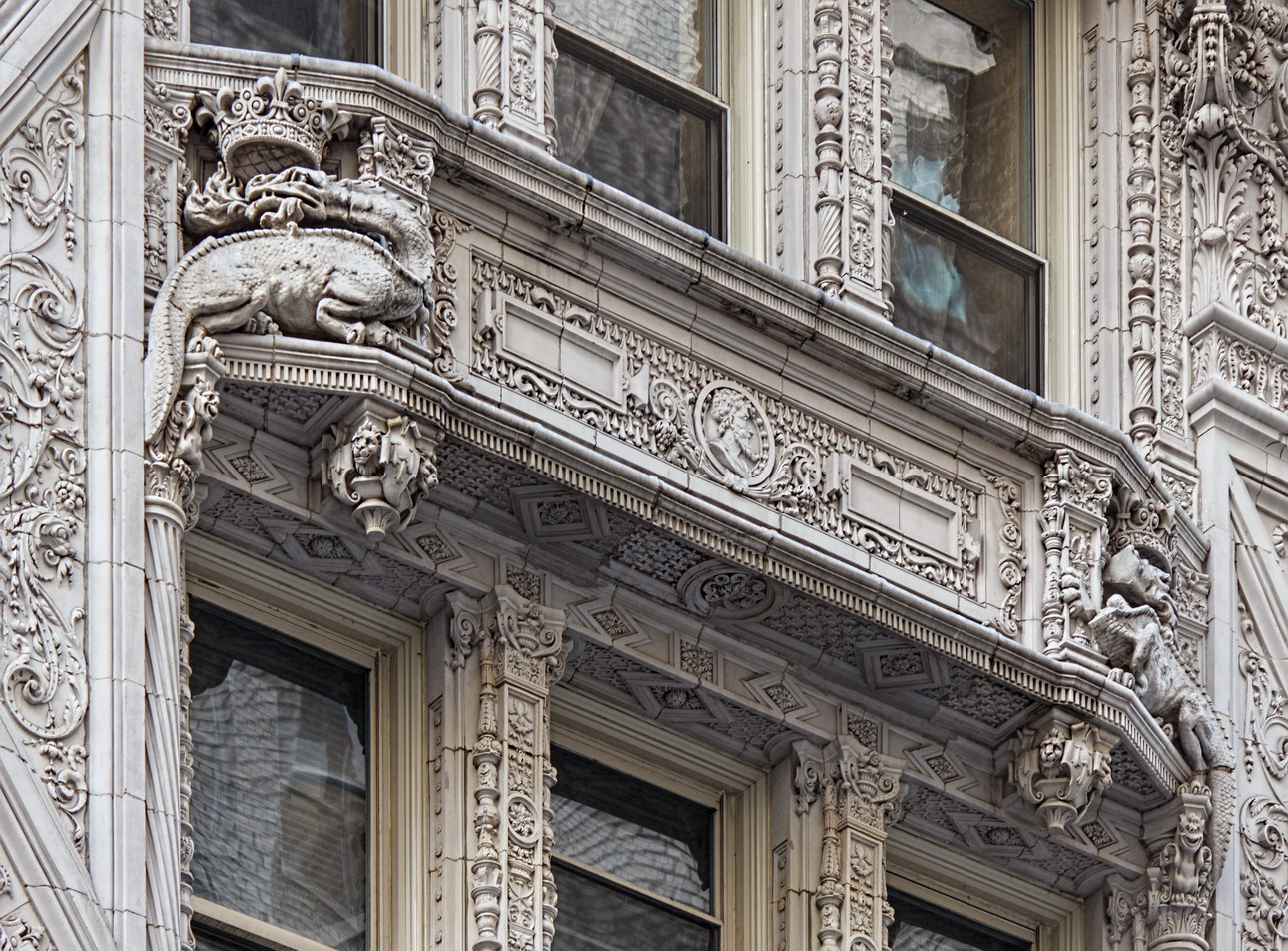
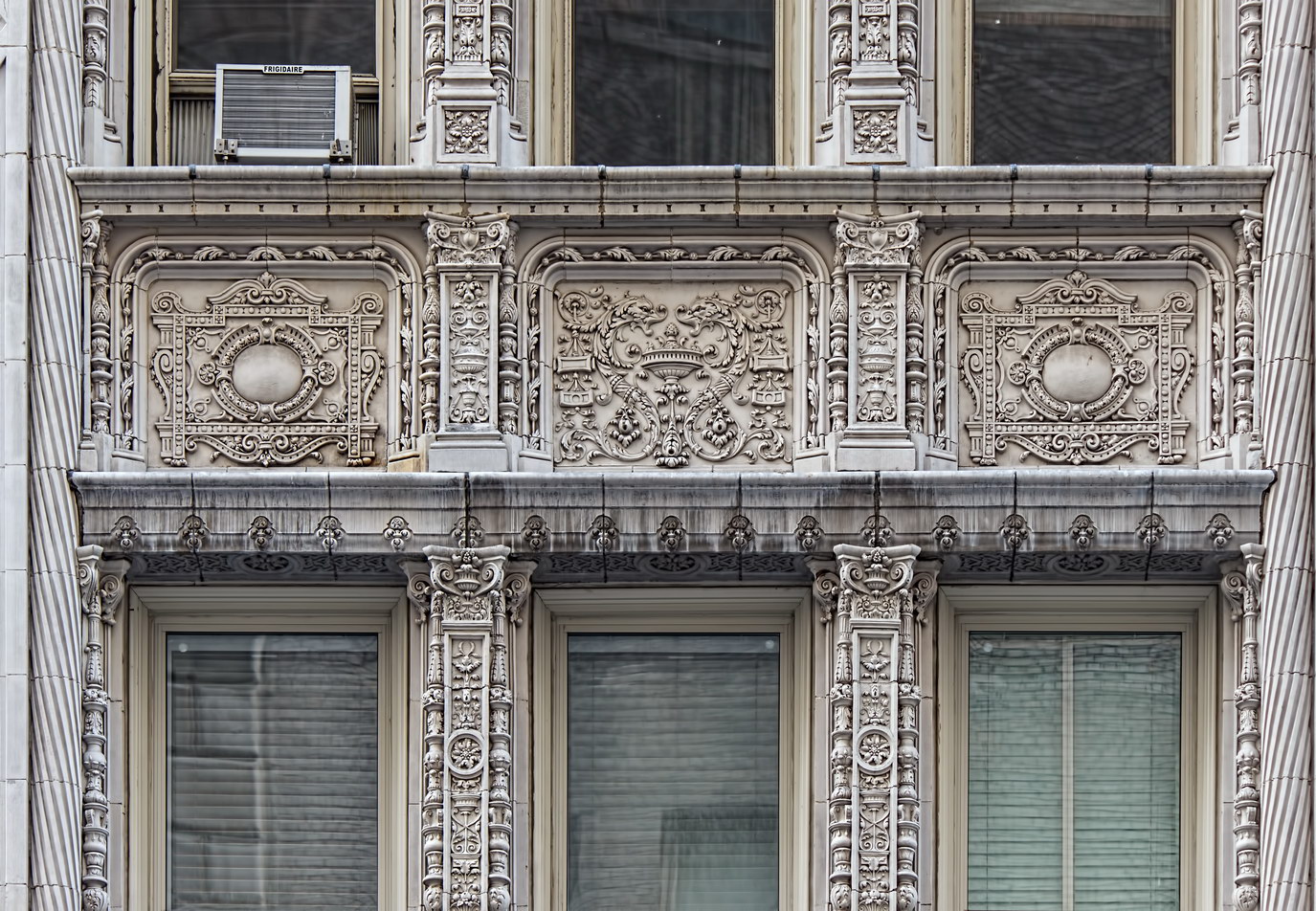
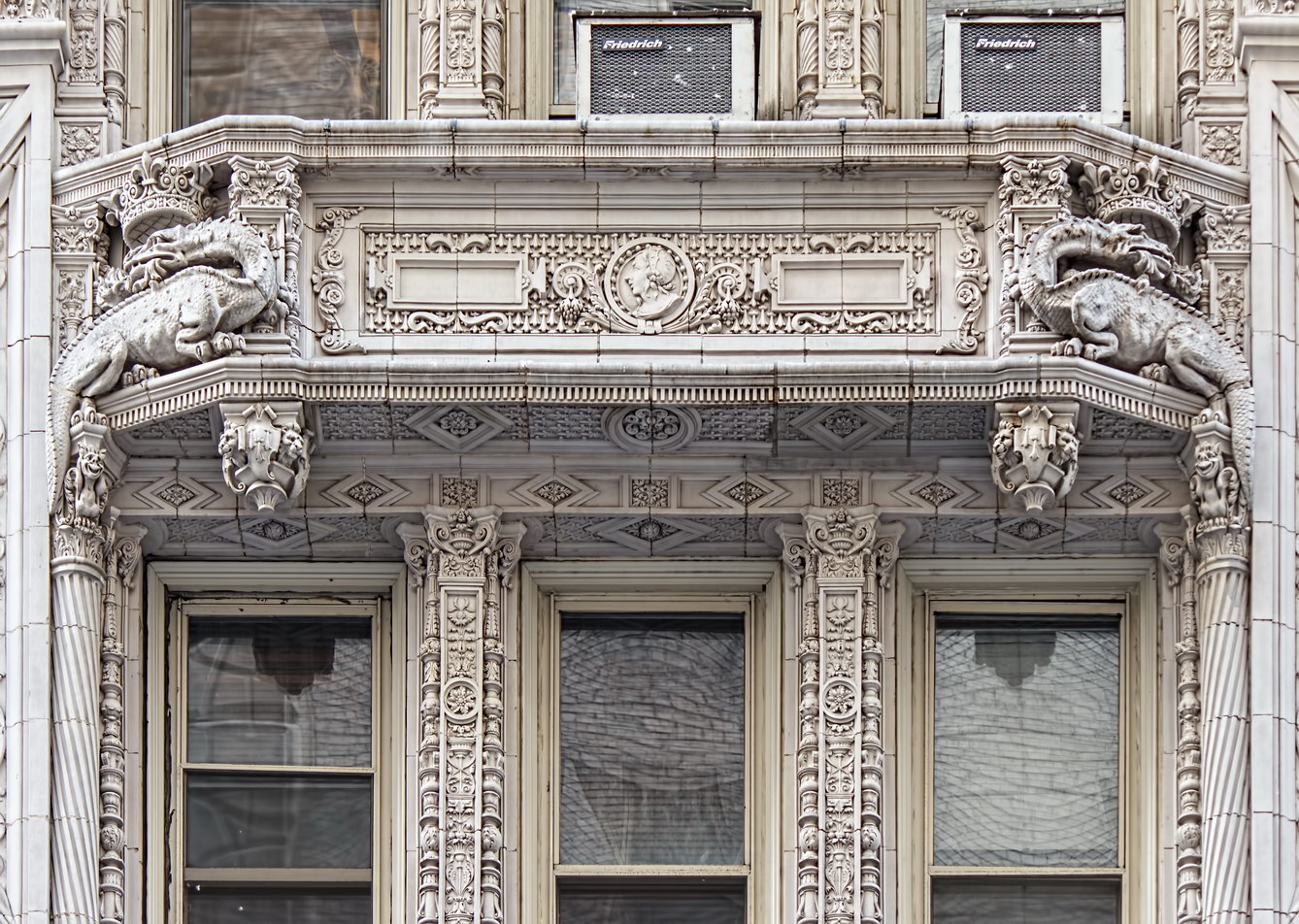
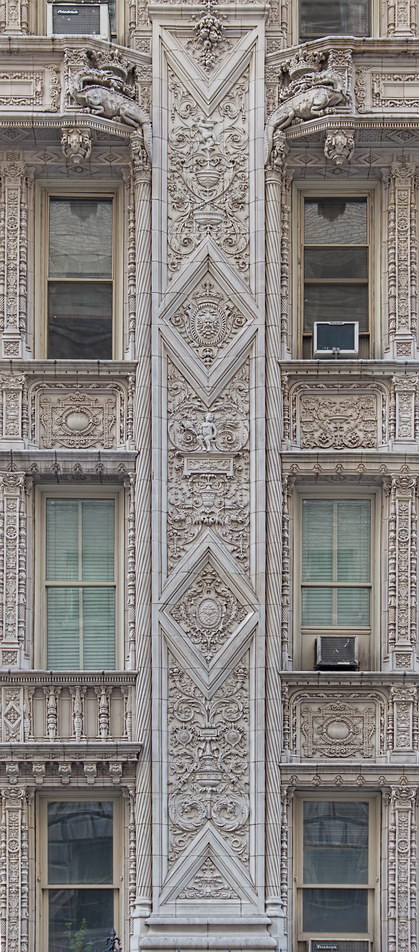
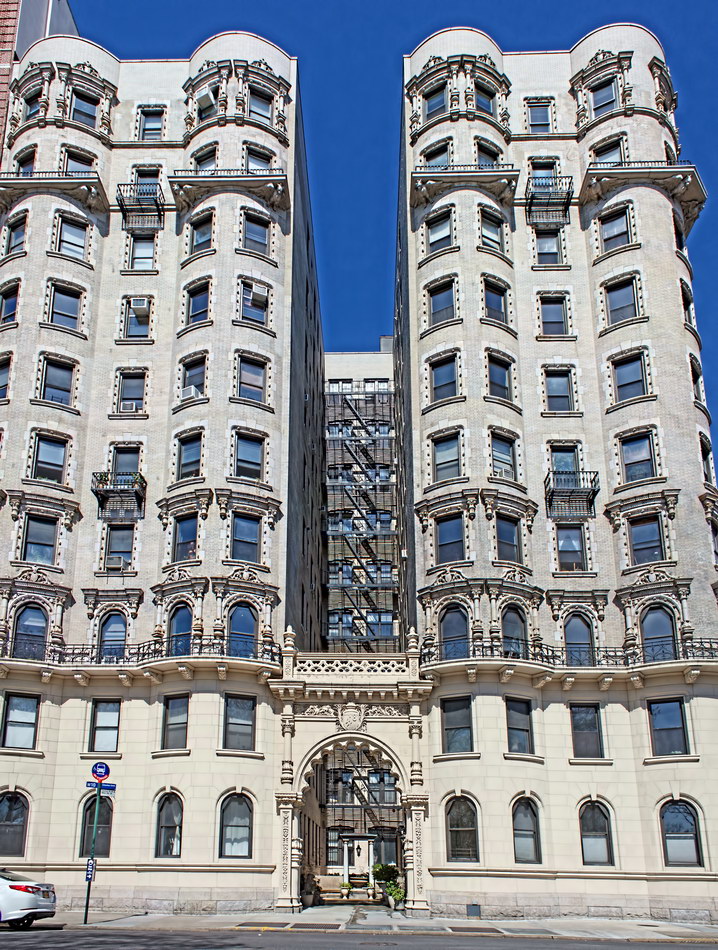
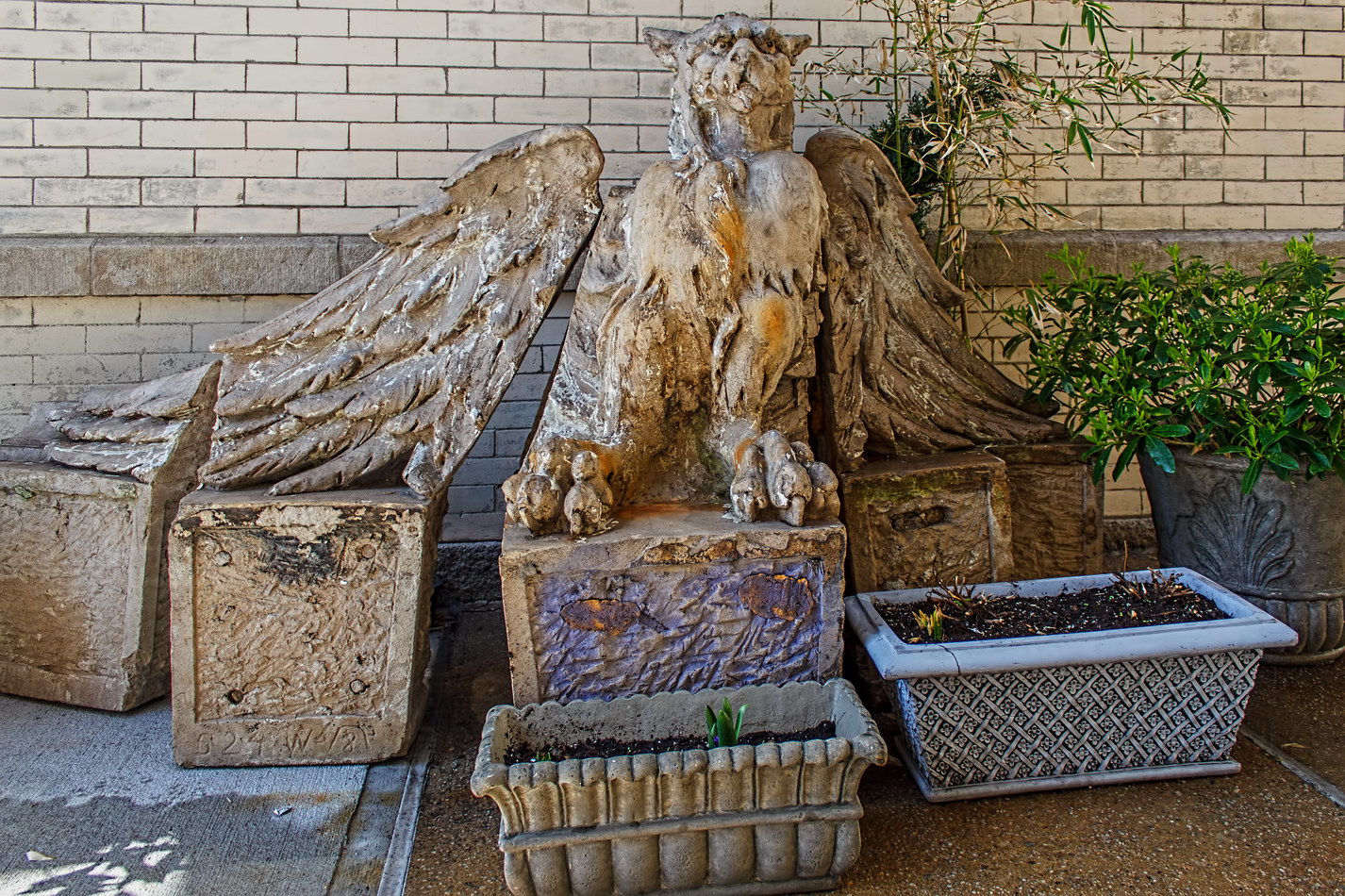
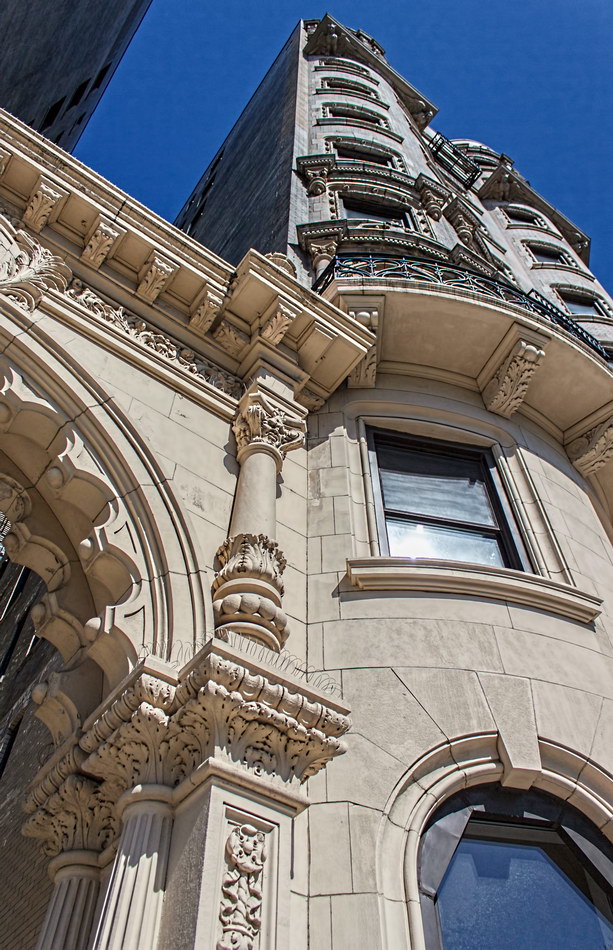
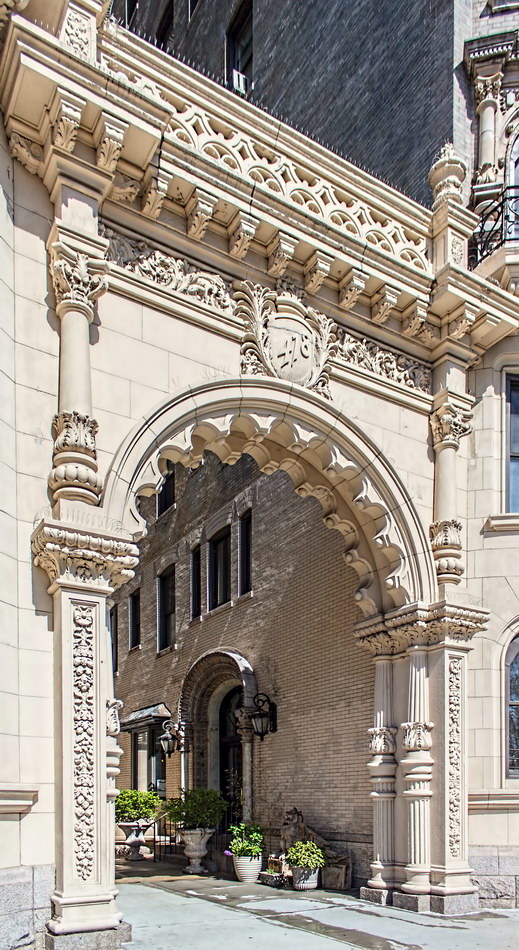
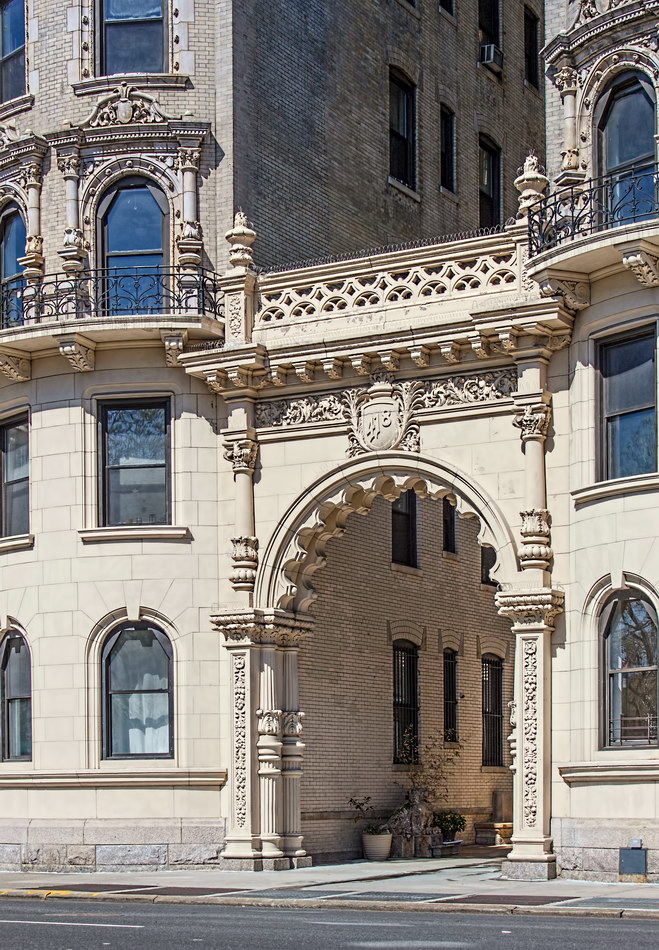
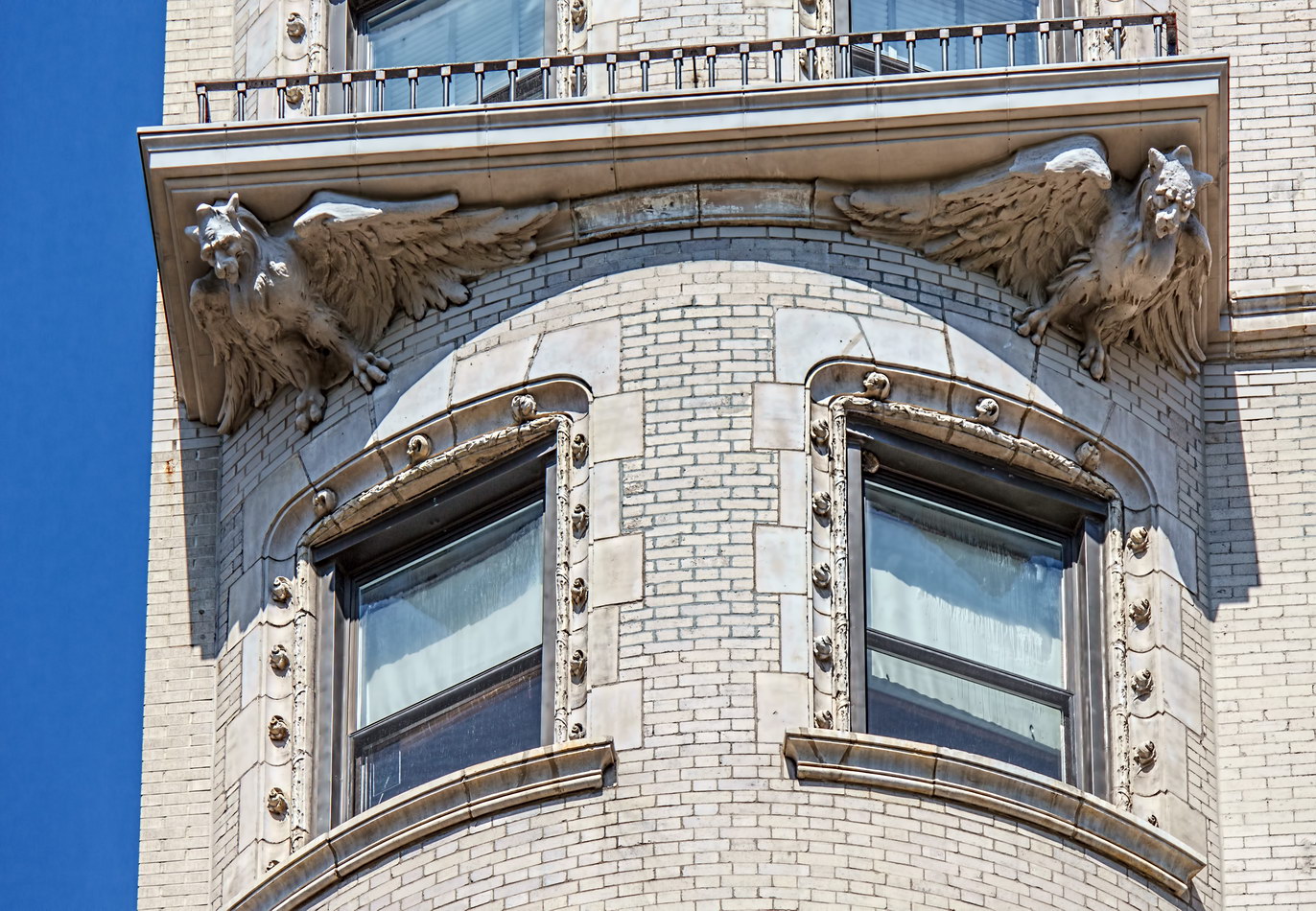
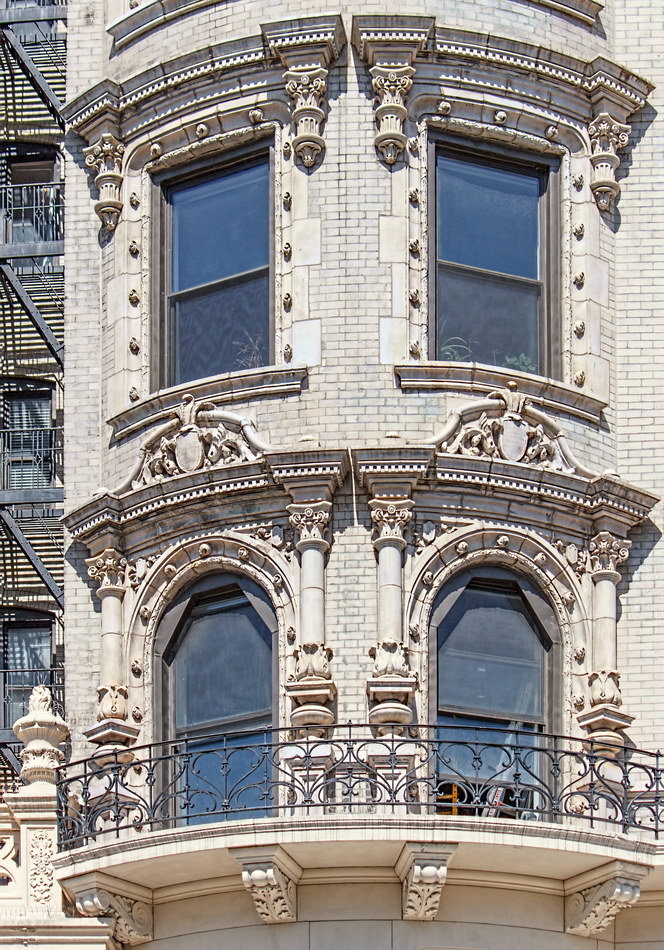
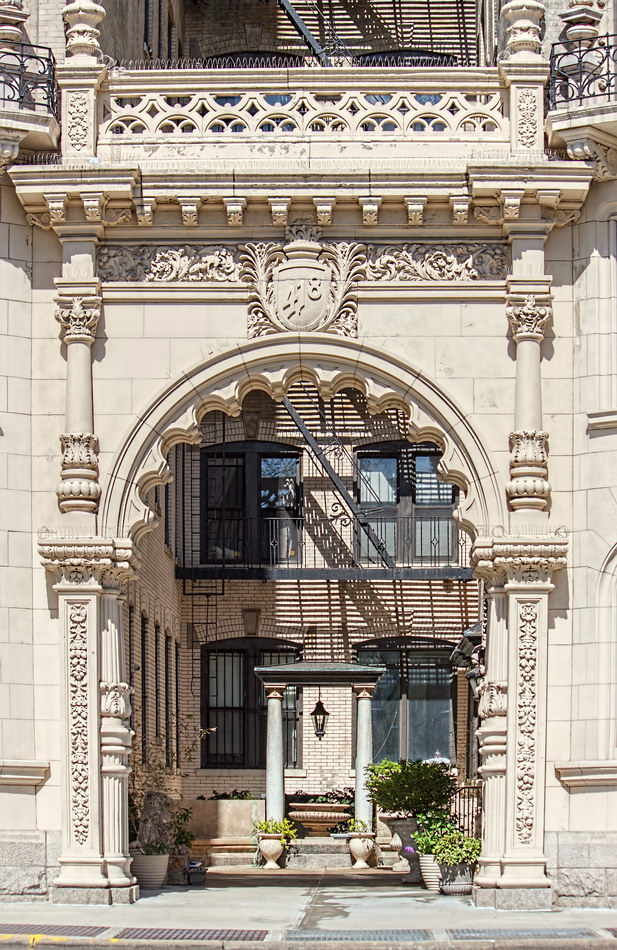
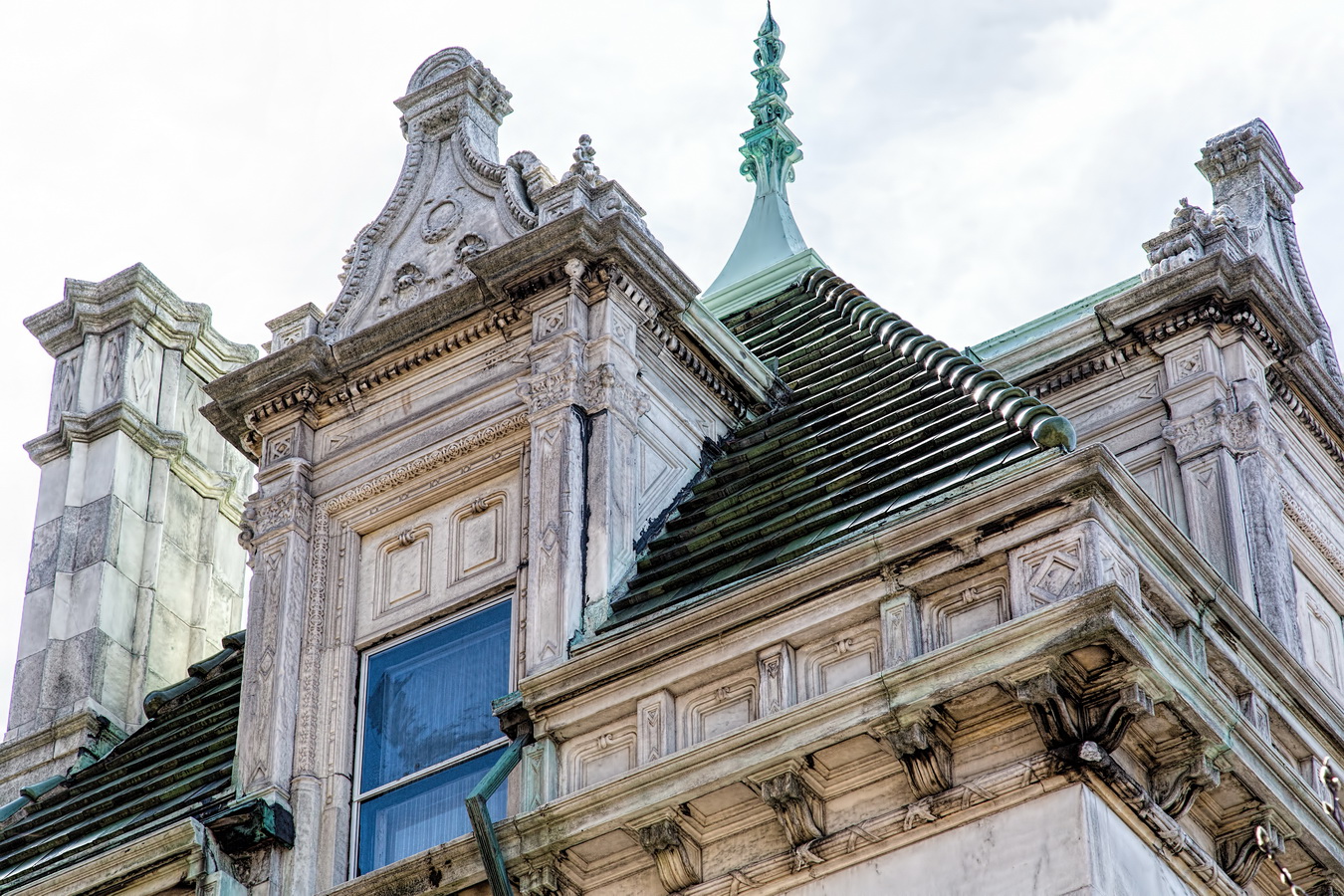
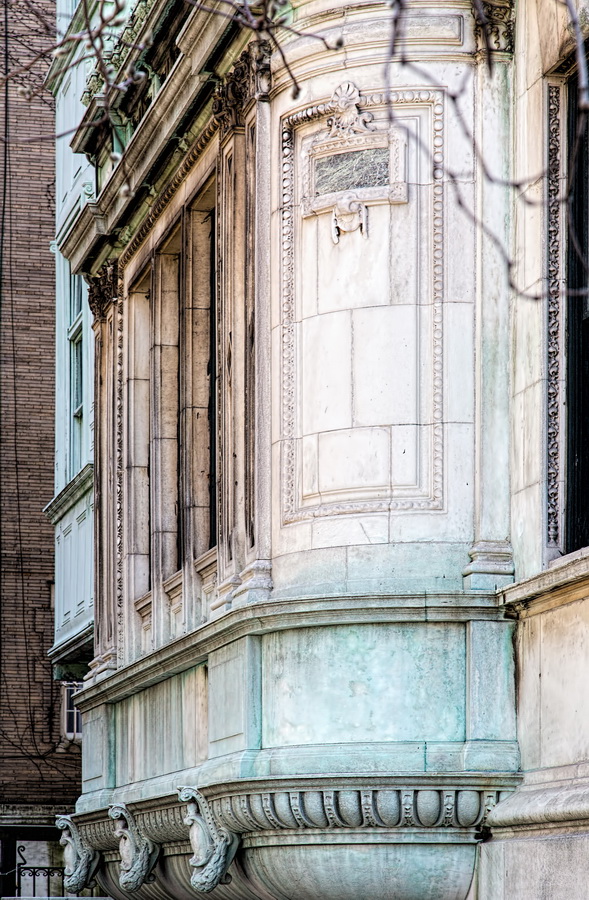
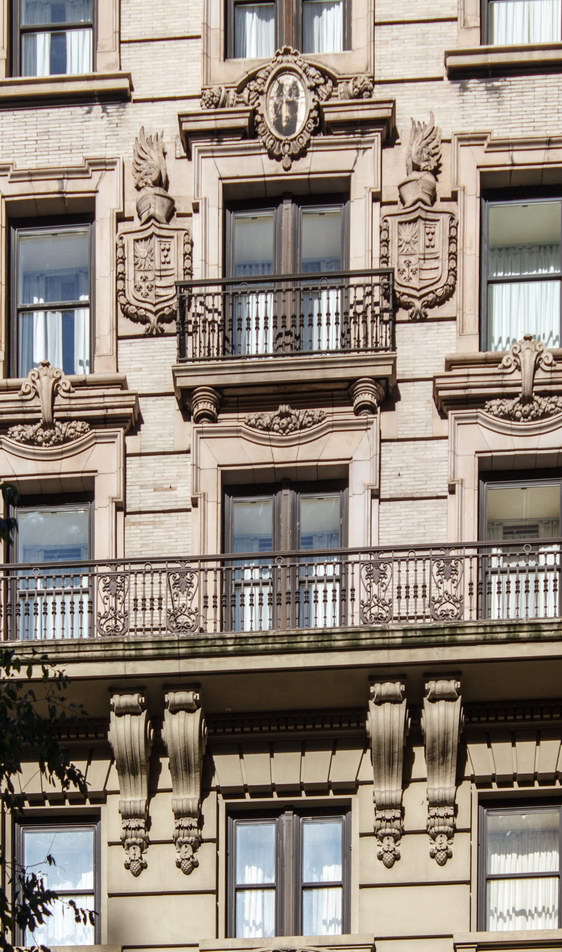
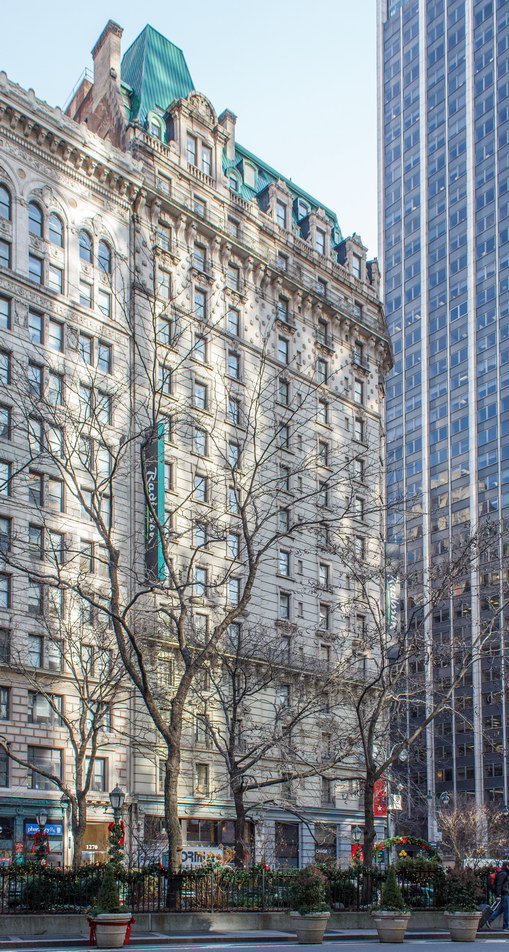
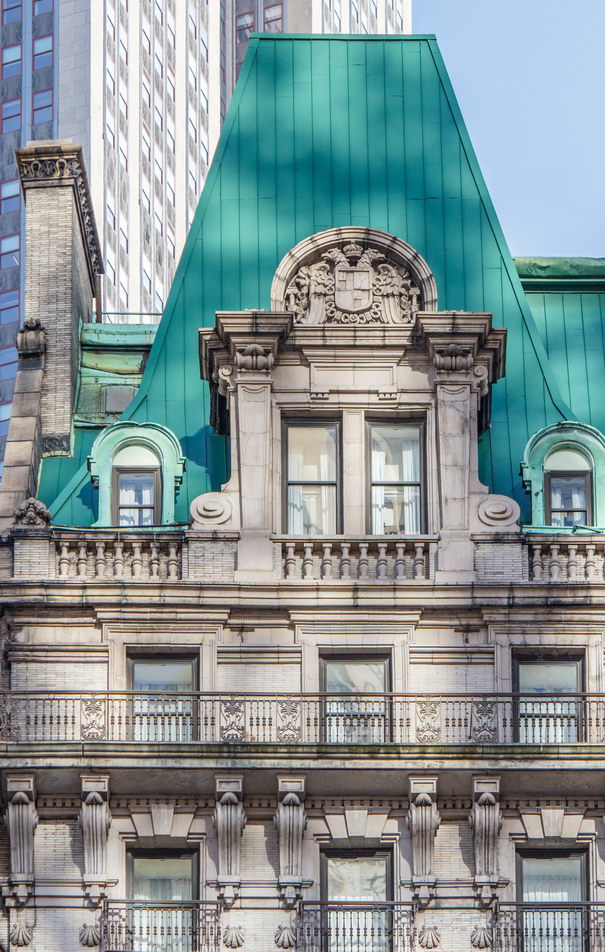
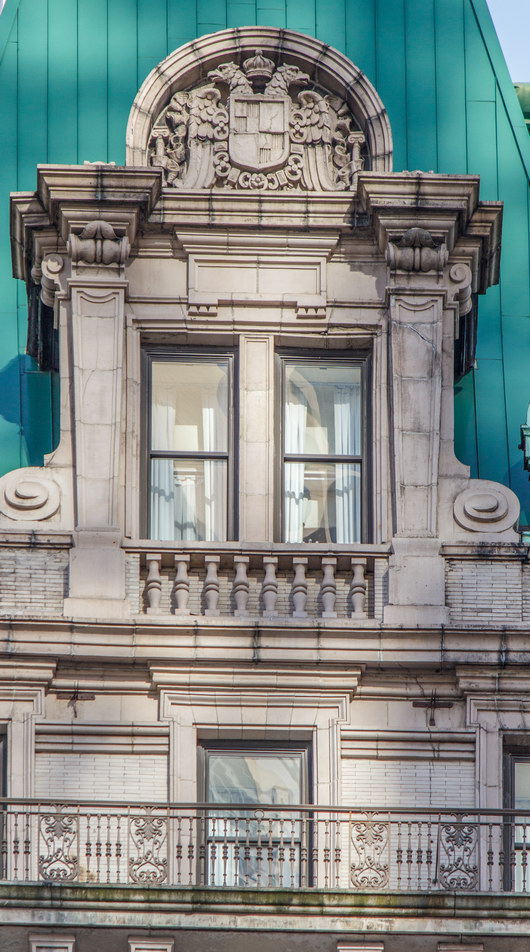
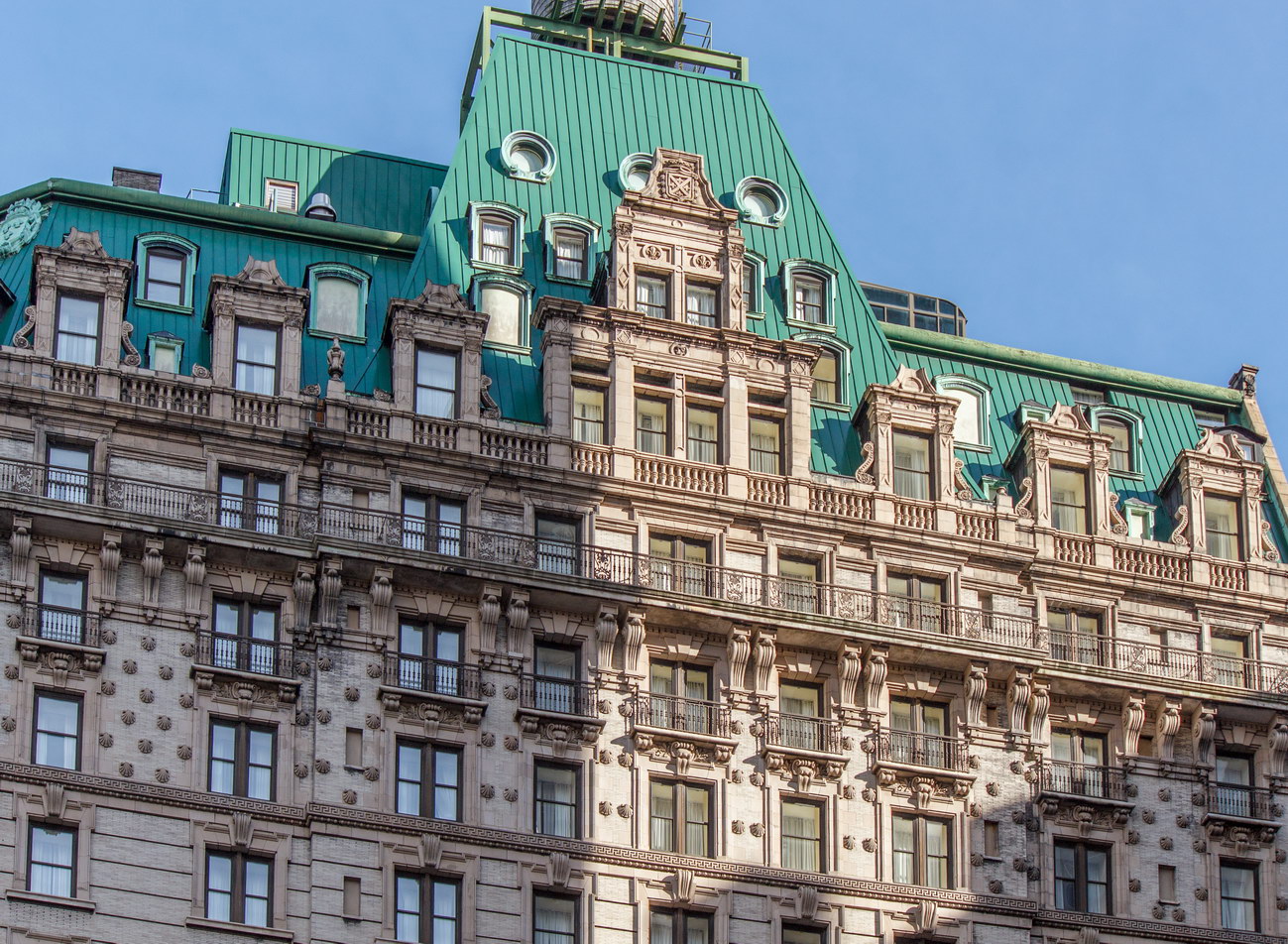
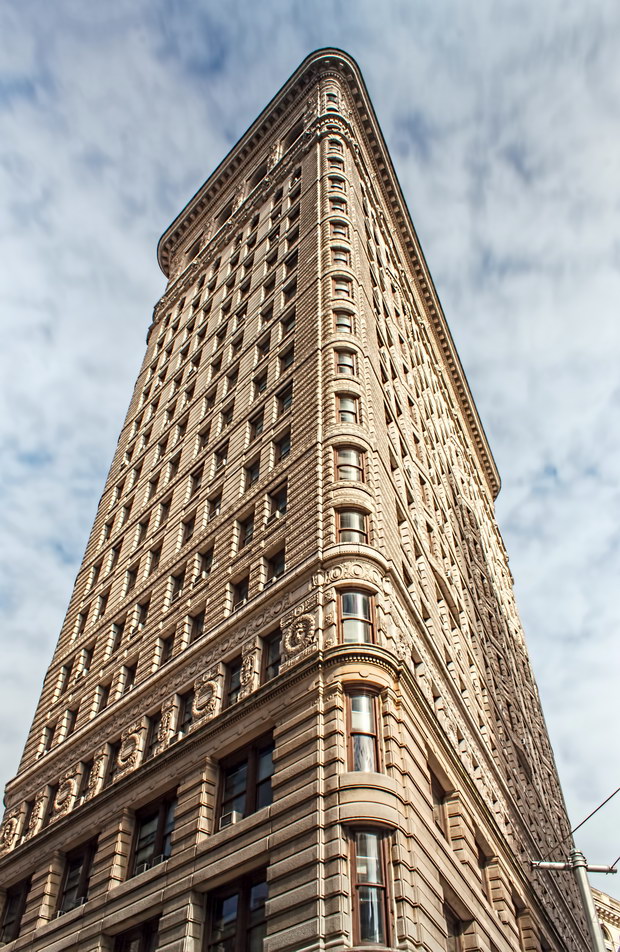
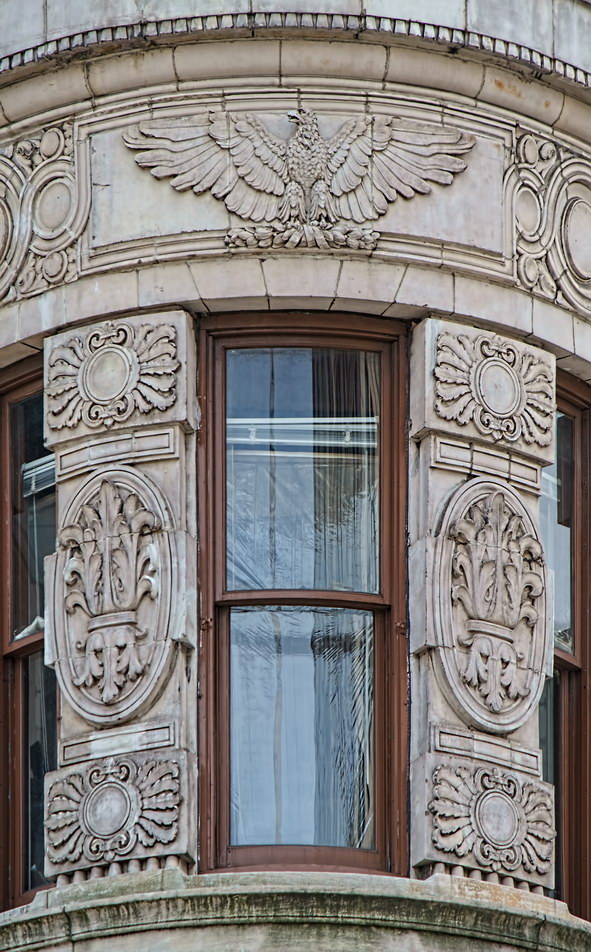
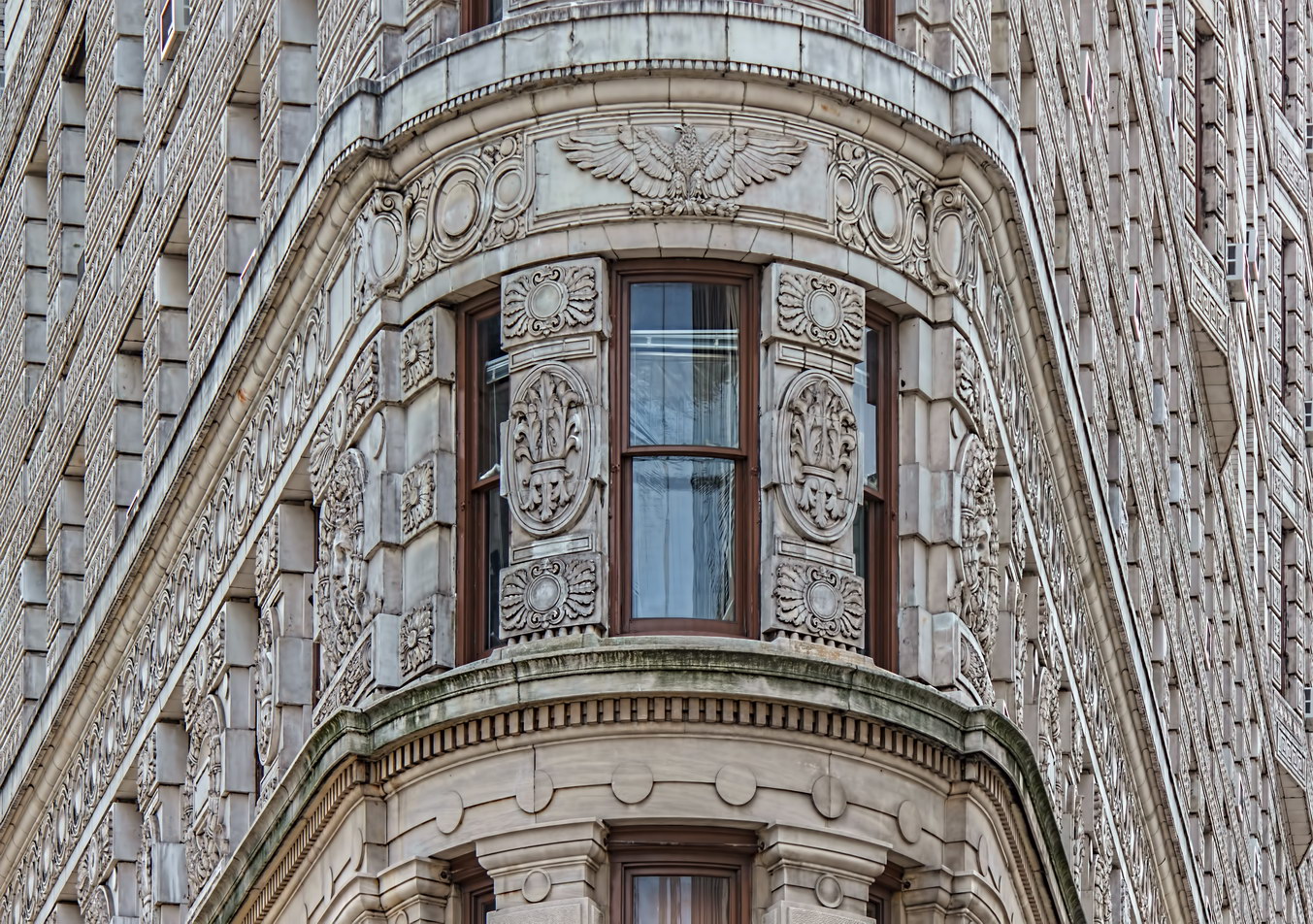
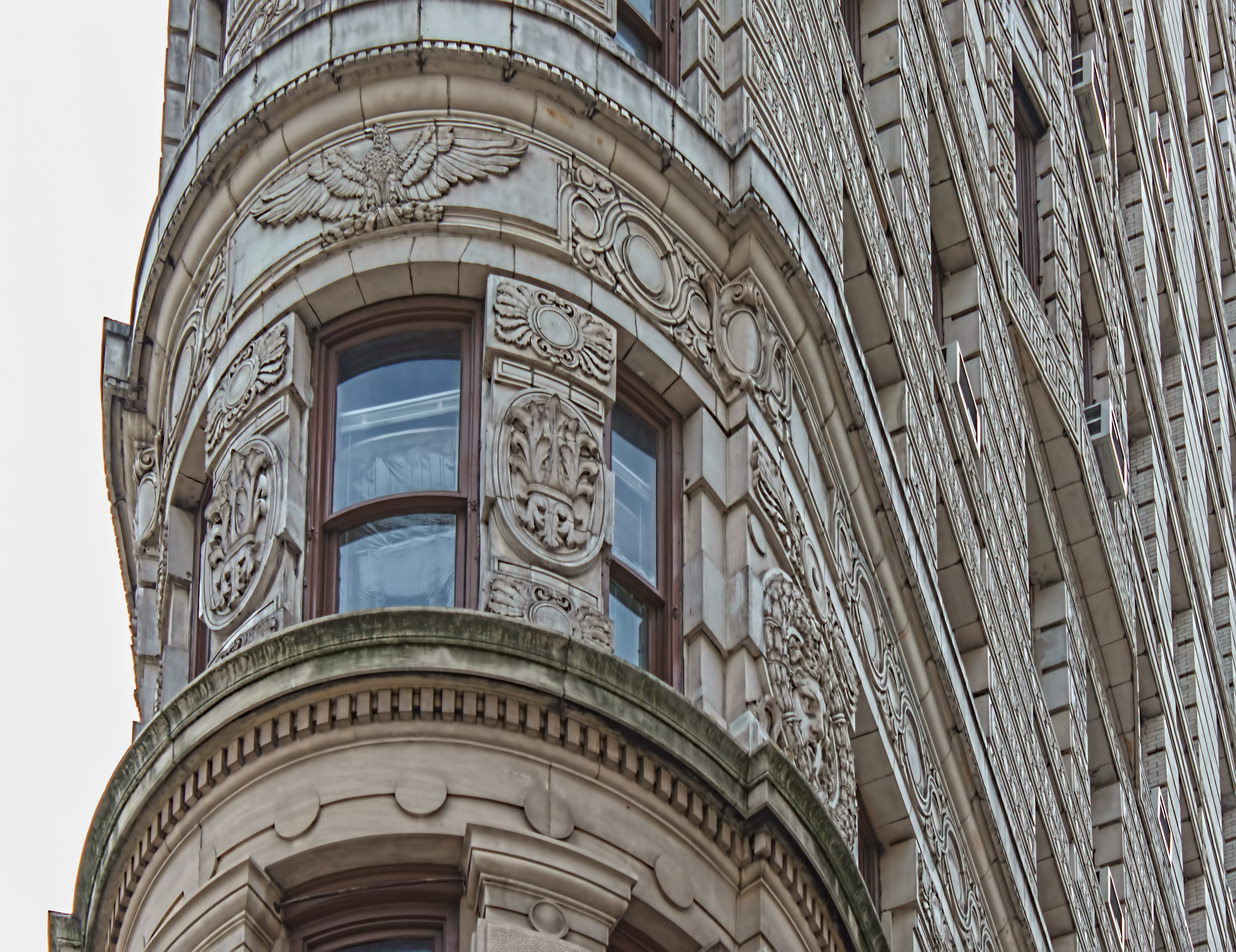
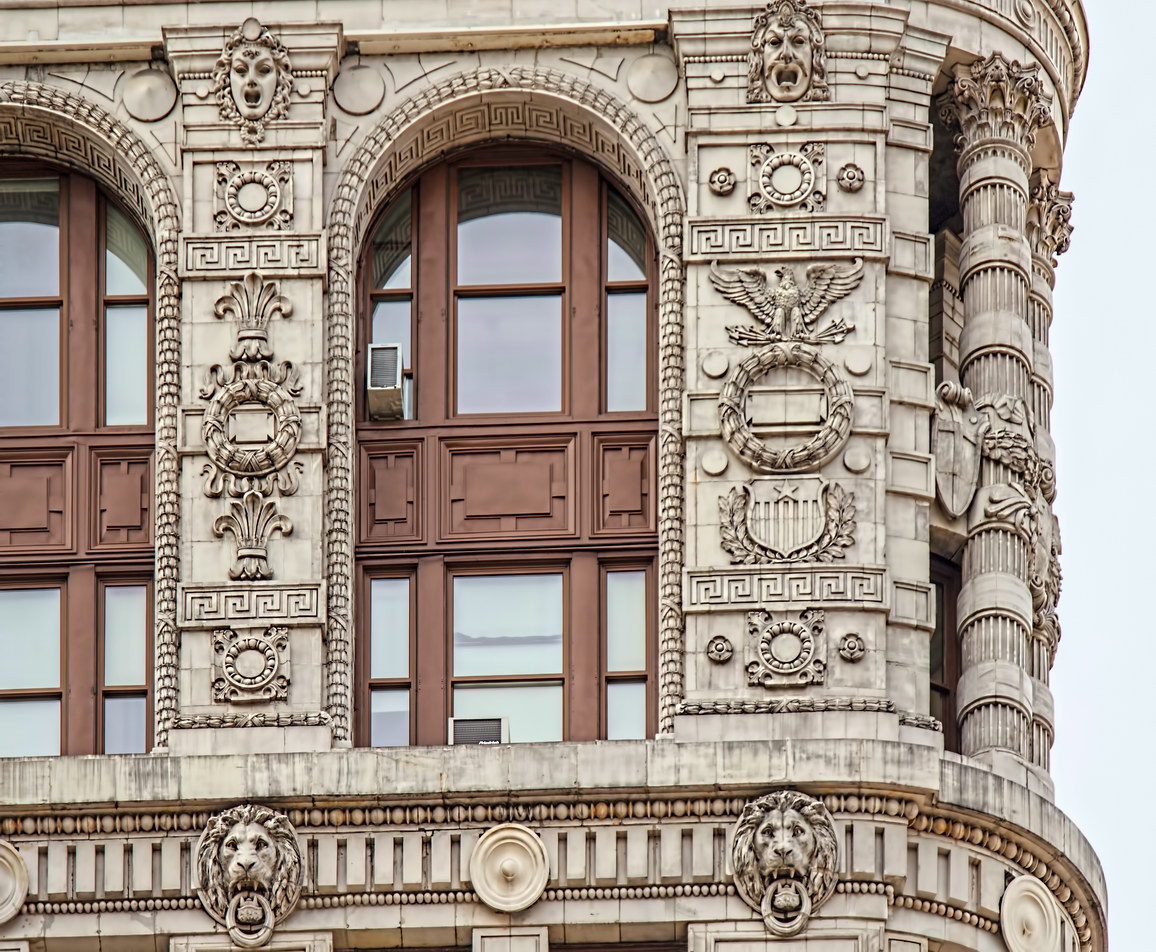
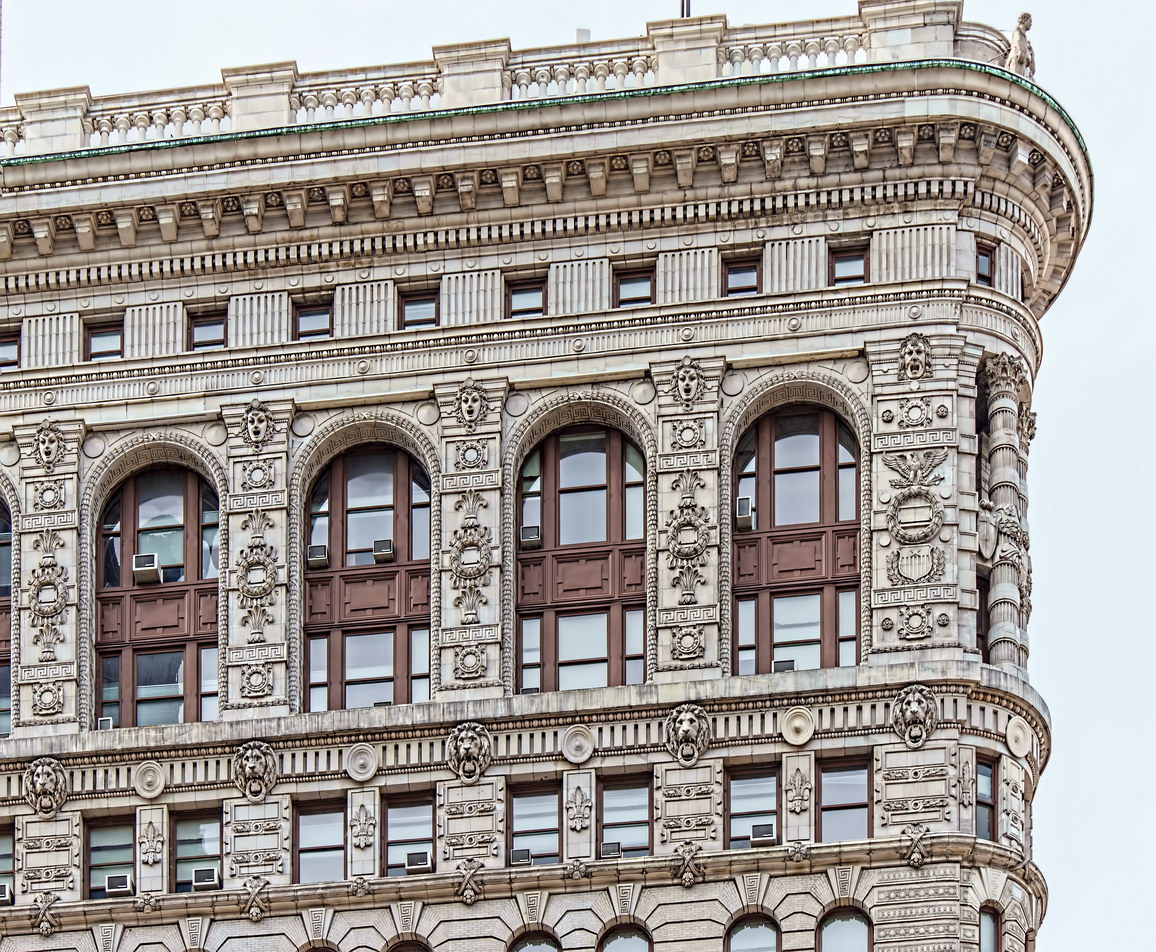
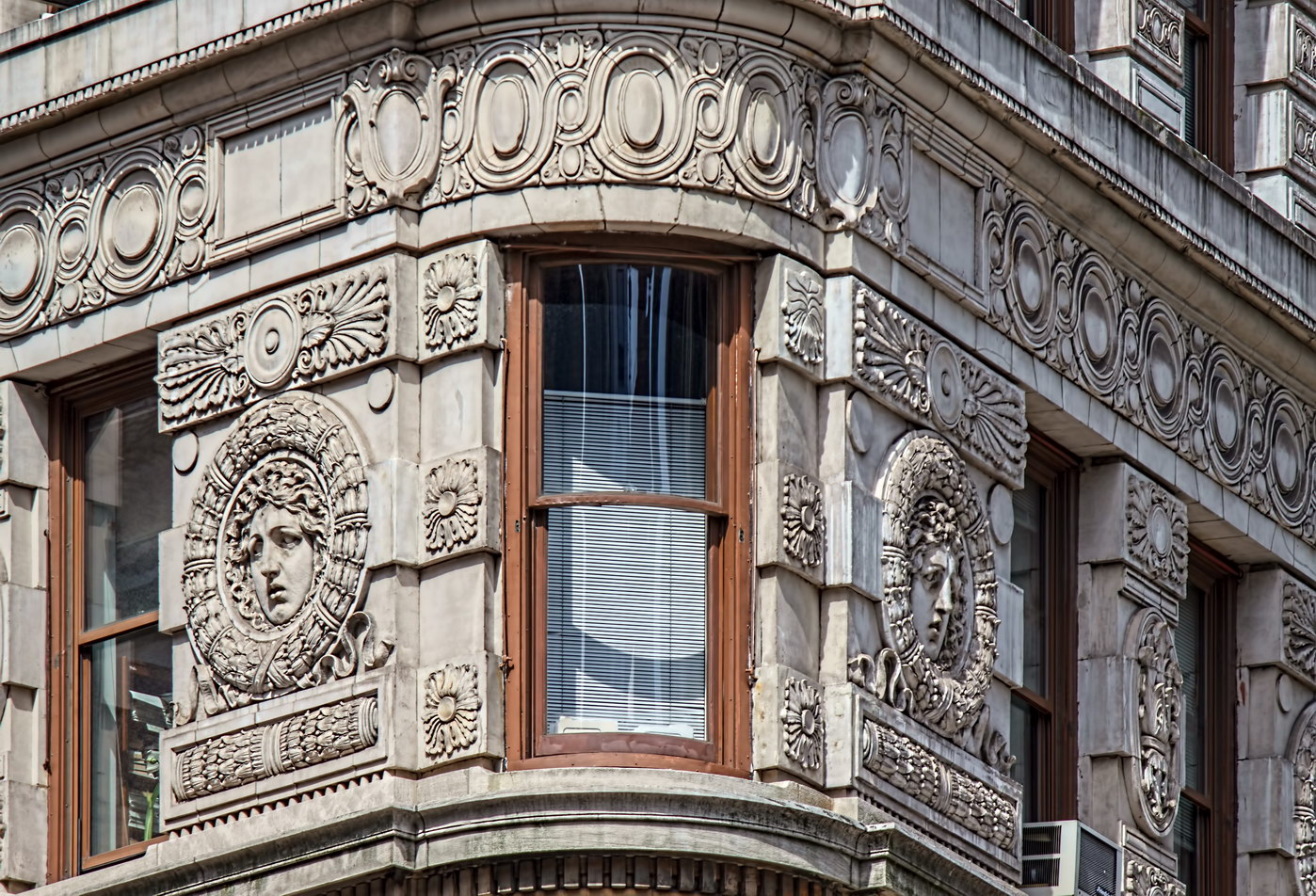
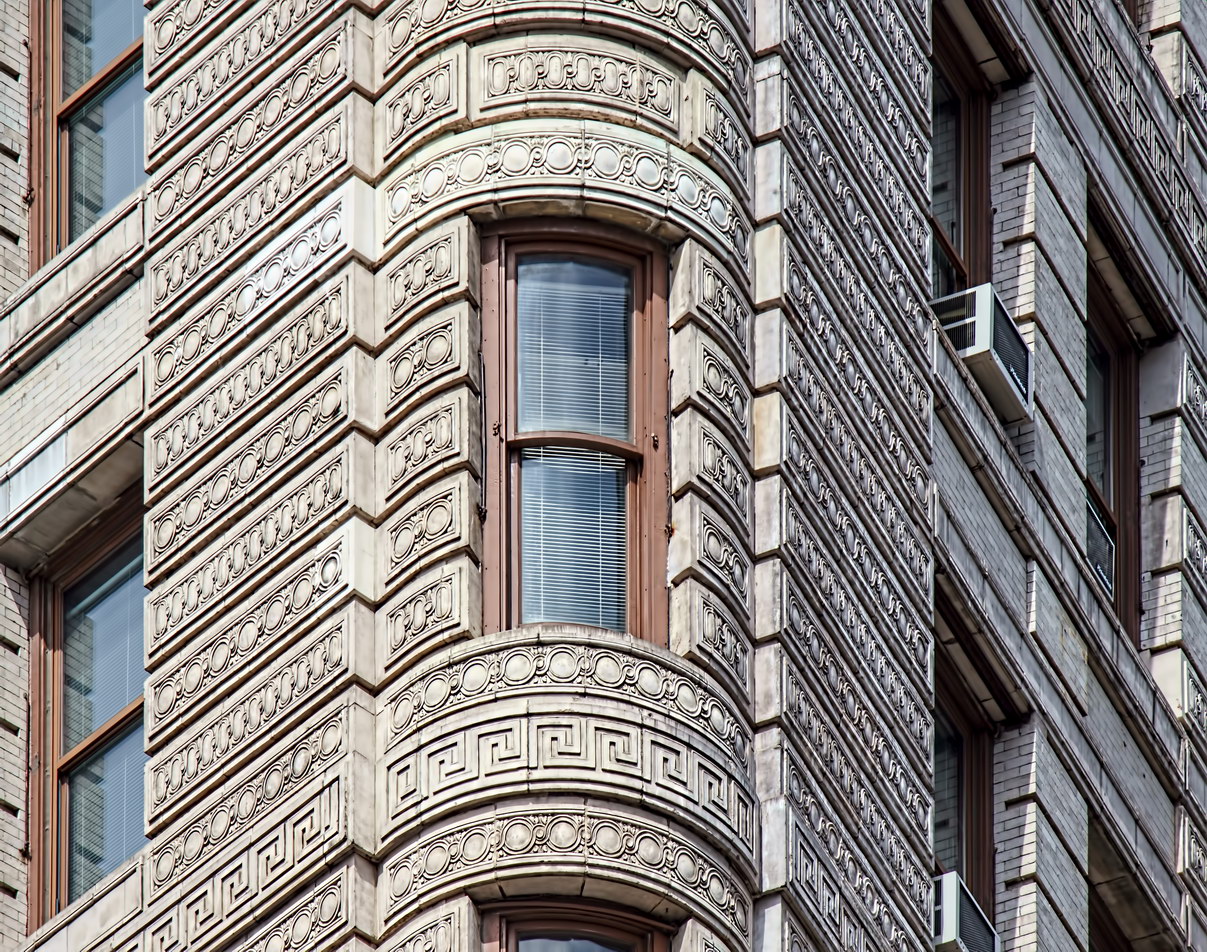
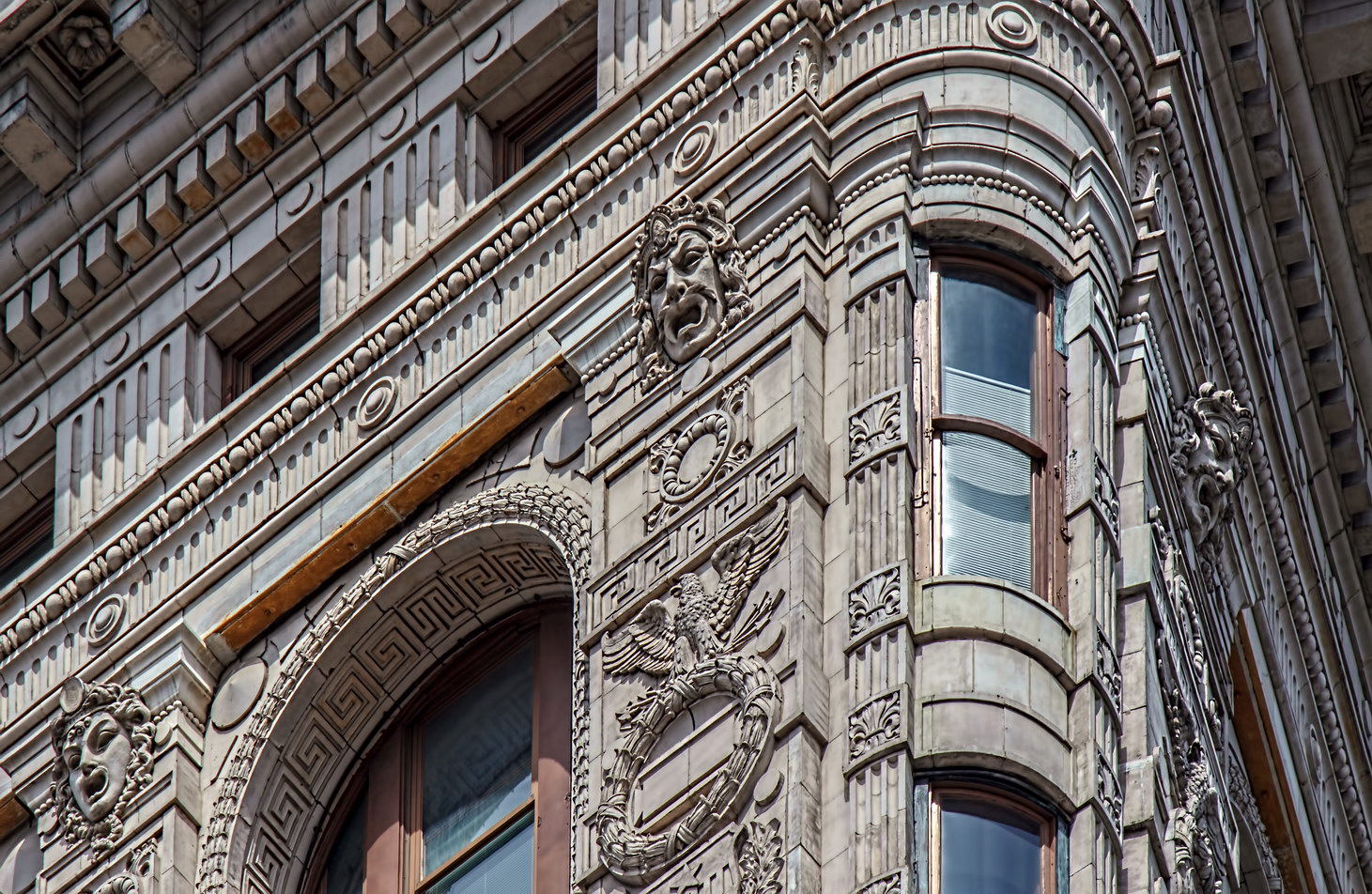
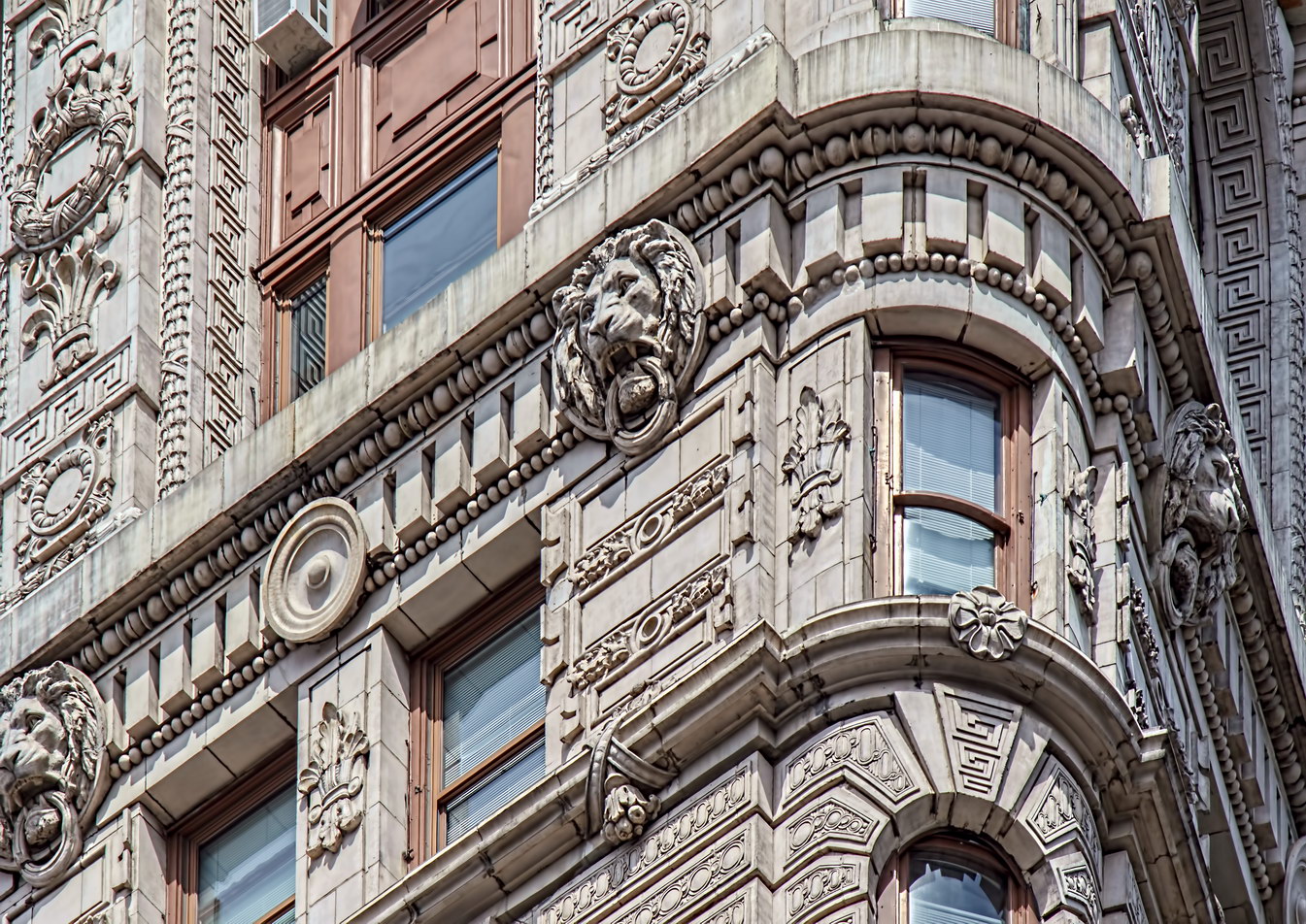
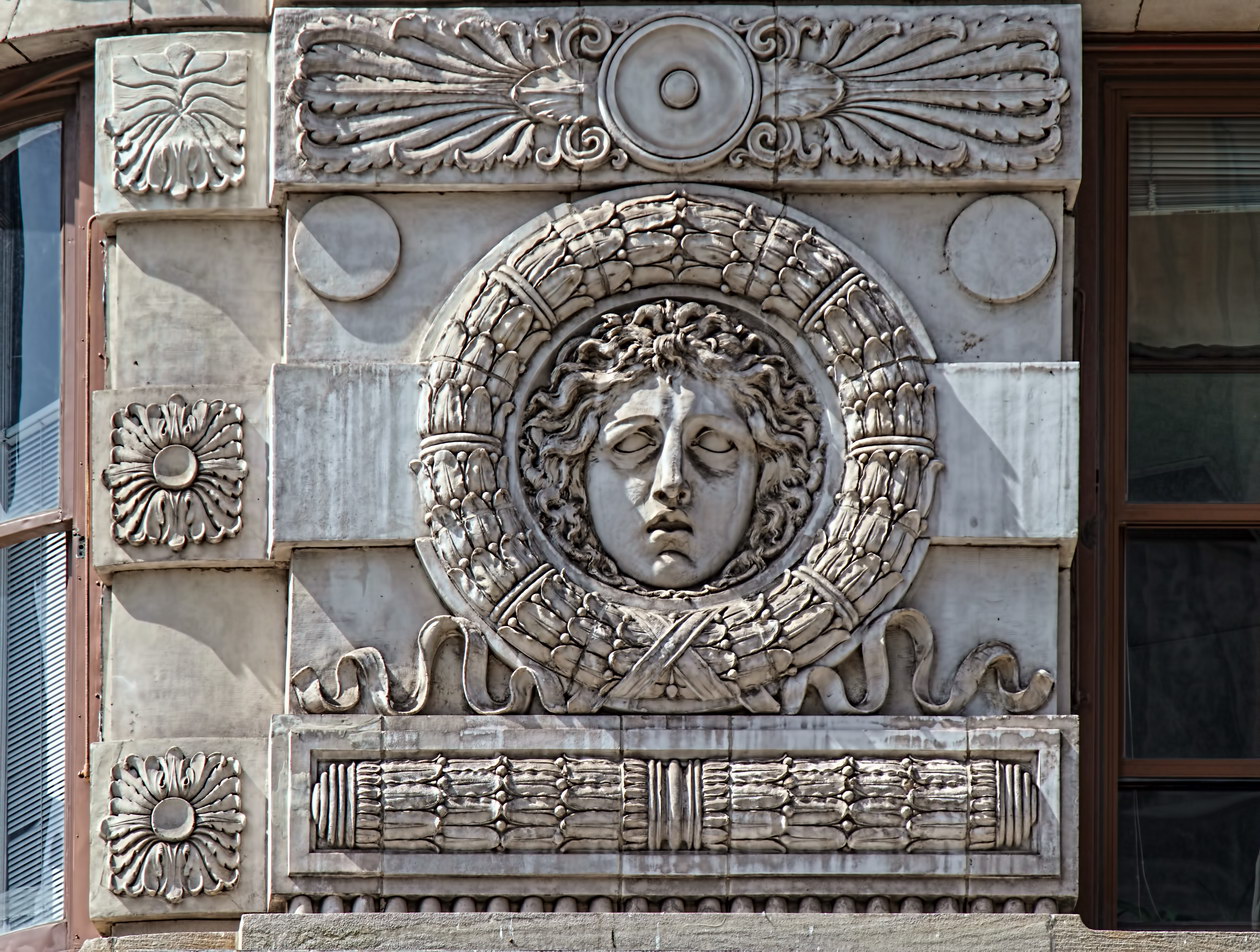
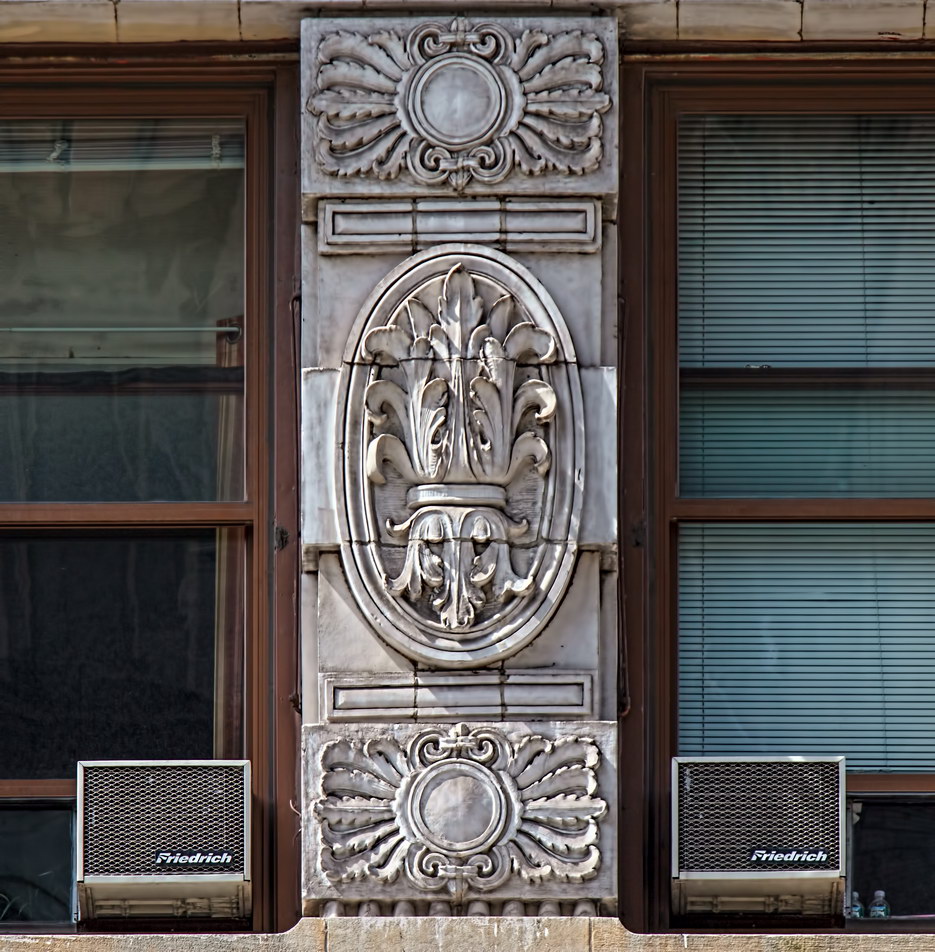
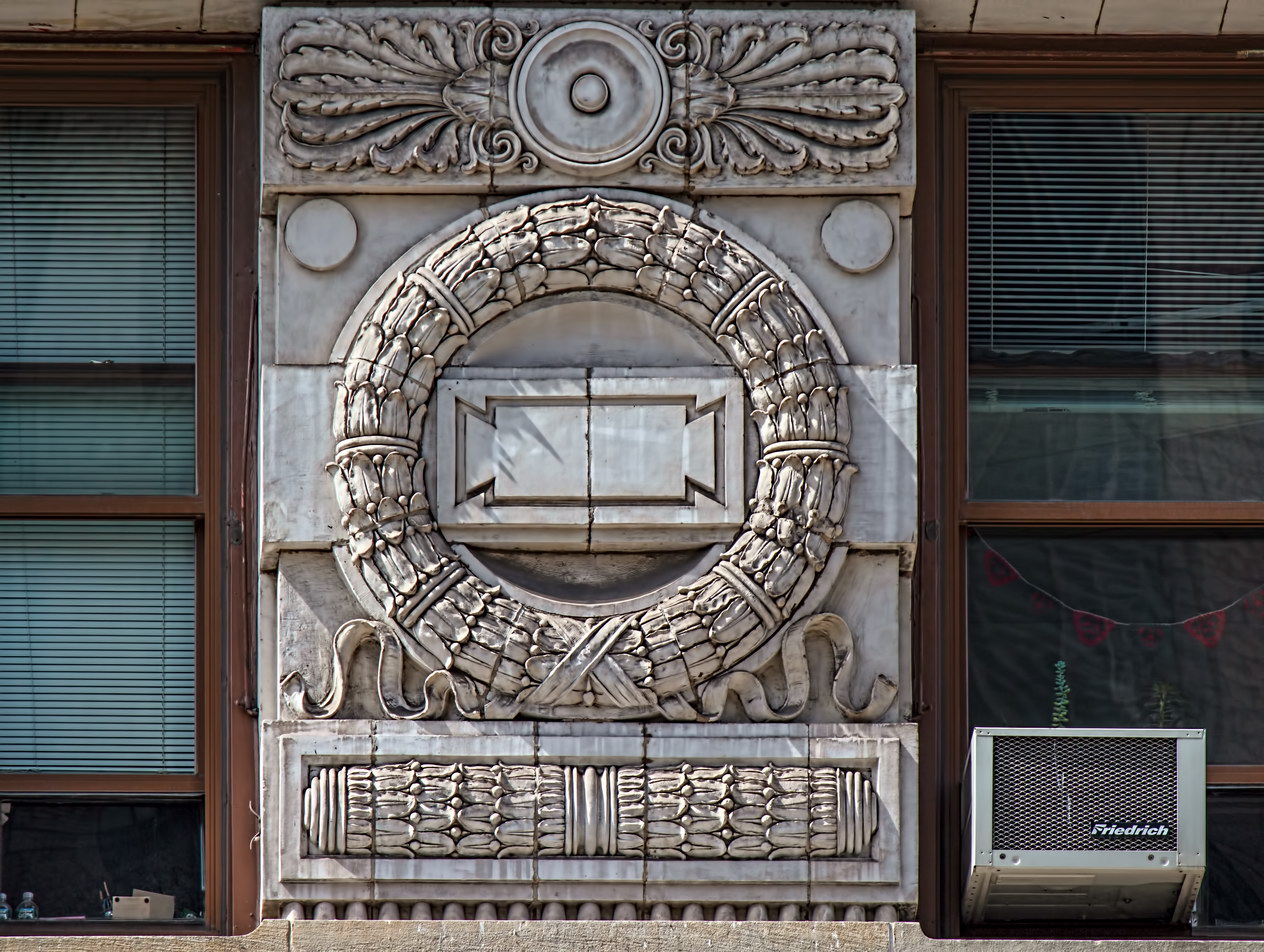
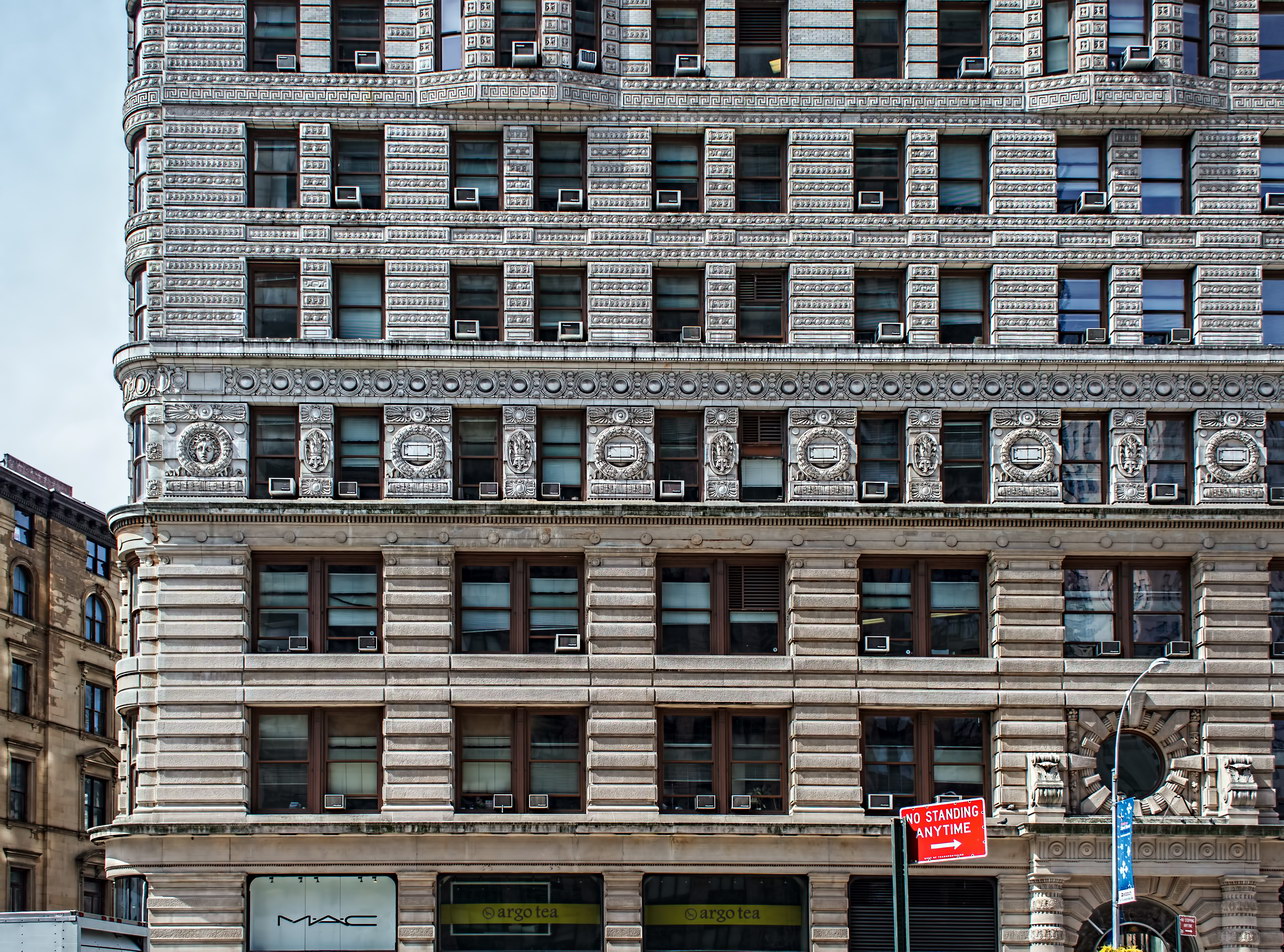
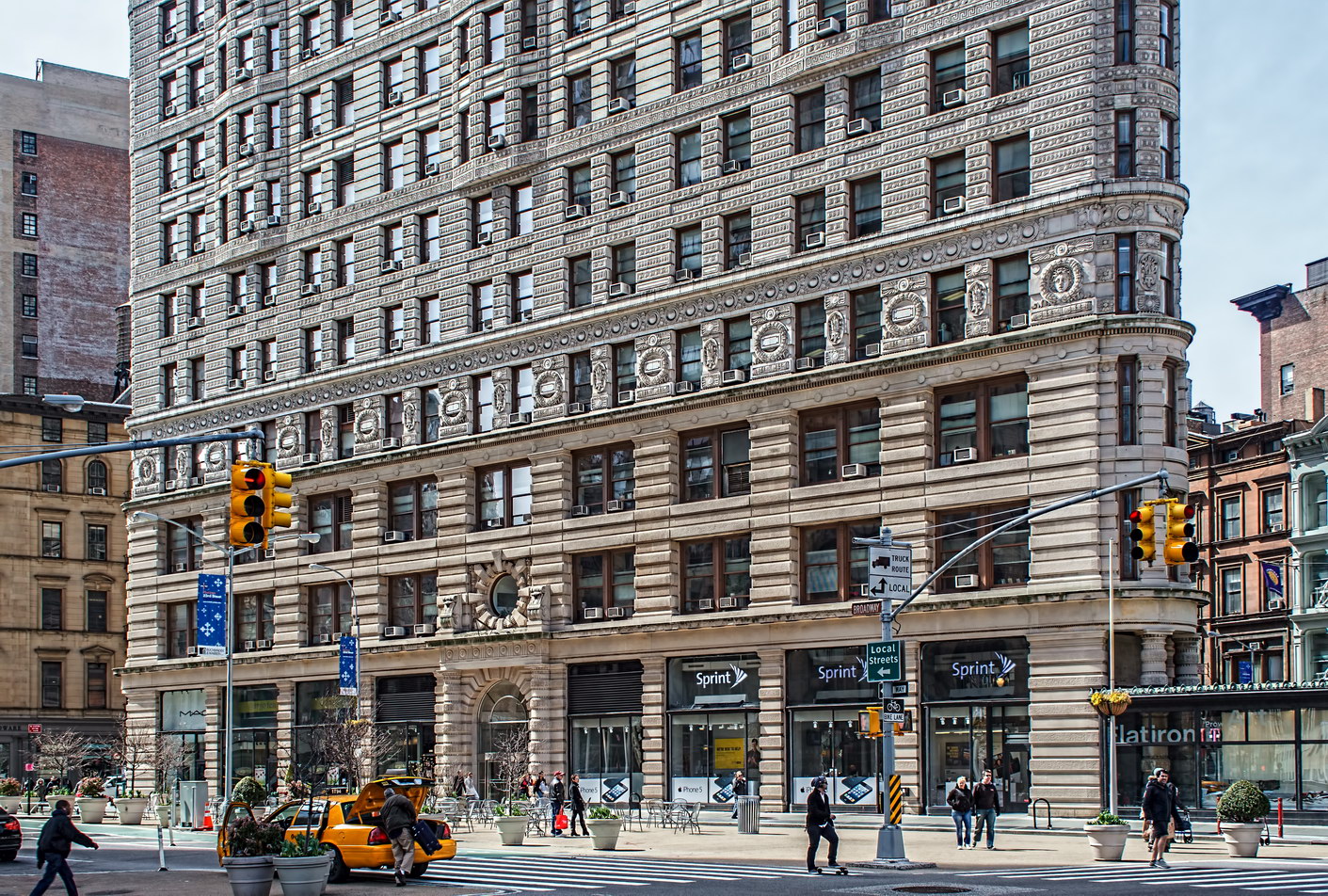
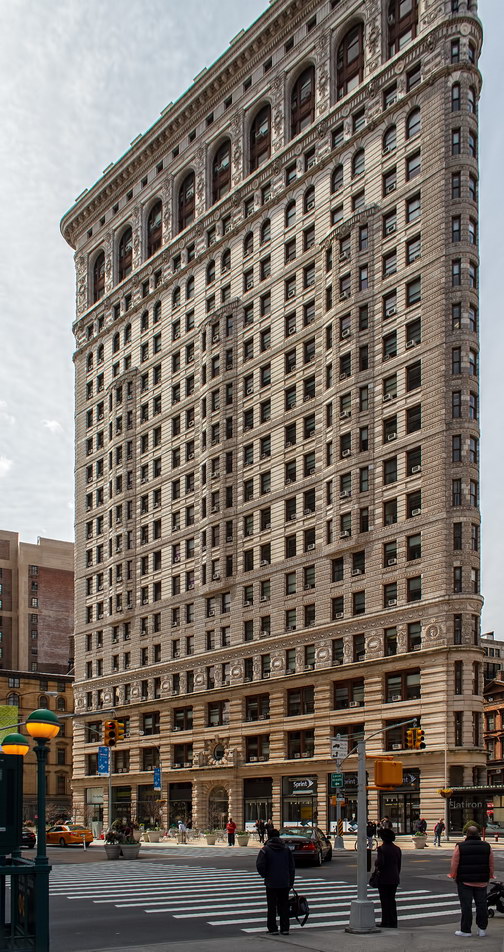
The structure’s design was a collaboration of New York-based architects Shultze & Weaver and Buchman & Kahn. Shultze & Weaver specialized in luxury hotels such as the Pierre and Waldorf-Astoria. The French Gothic/French Renaissance tower is among New York’s most distinctive spires, hiding a water tank above the gargoyles. There is an observation platform at the very top – though you’d have to be brave and a climber to reach it!
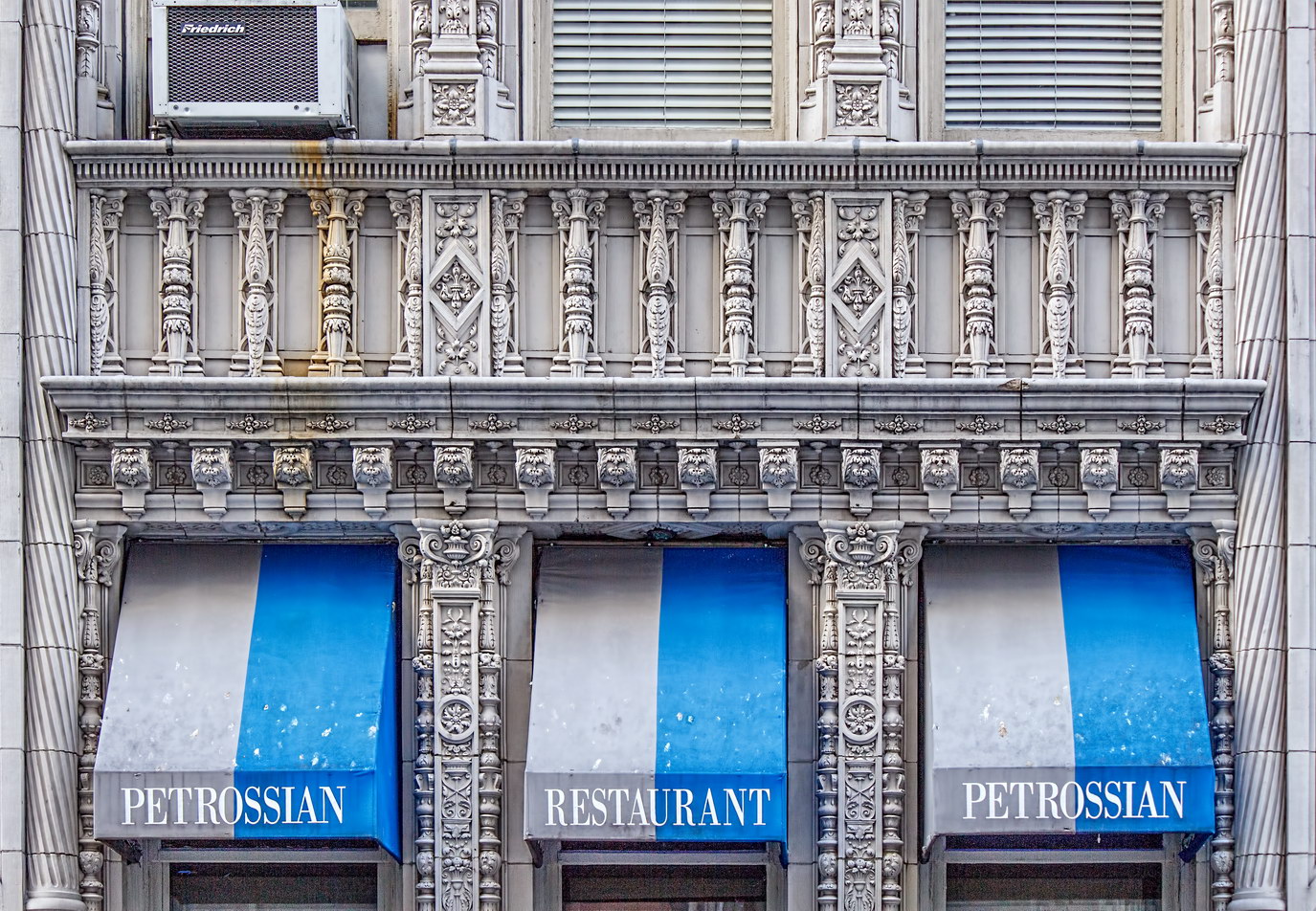
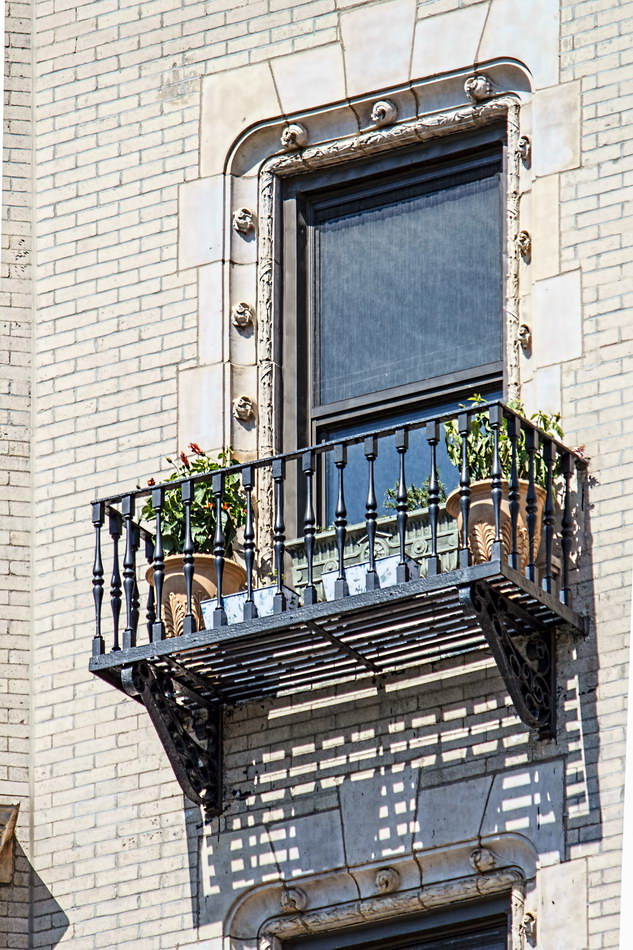
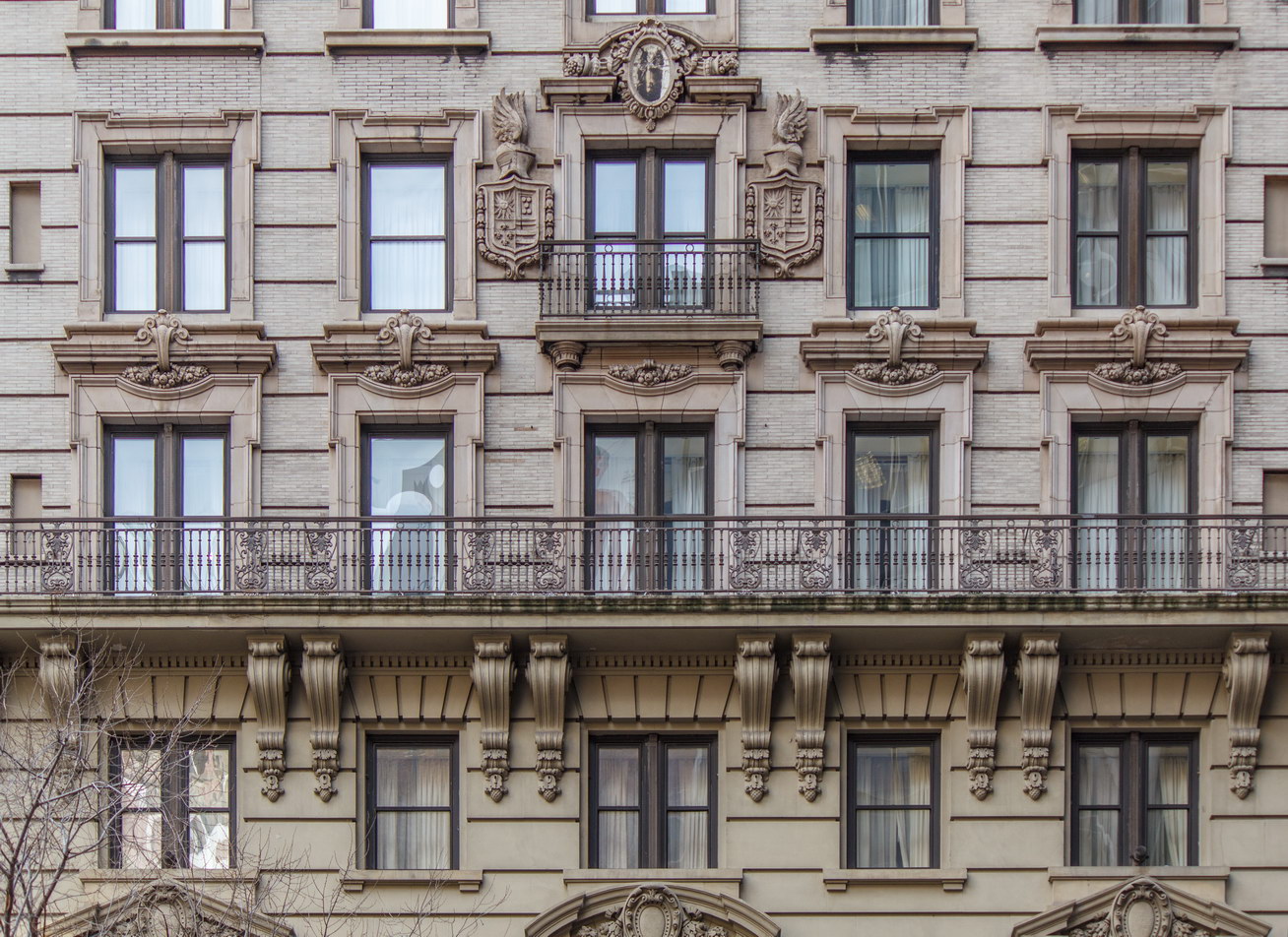
While the Sherry Netherland’s public personna is a hotel, it has only 54 rooms and suites; 165 co-op apartments make up the bulk of the building.
Sherry Netherland Vital Statistics
- Location: 751 Fifth Avenue at E 59th Street
- Year completed: 1927
- Architect: Shultze & Weaver and Buchman & Kahn
- Floors: 48
- Style: French Gothic/French Renaissance
Sherry Netherland Suggested Reading
- Wikipedia entry
- City Realty review
- Sherry Netherland website
- Architectural Digest article: New York Attitude (renovating a Sherry Netherland apartment)
- NYC Architecture – Top 10 Hotels

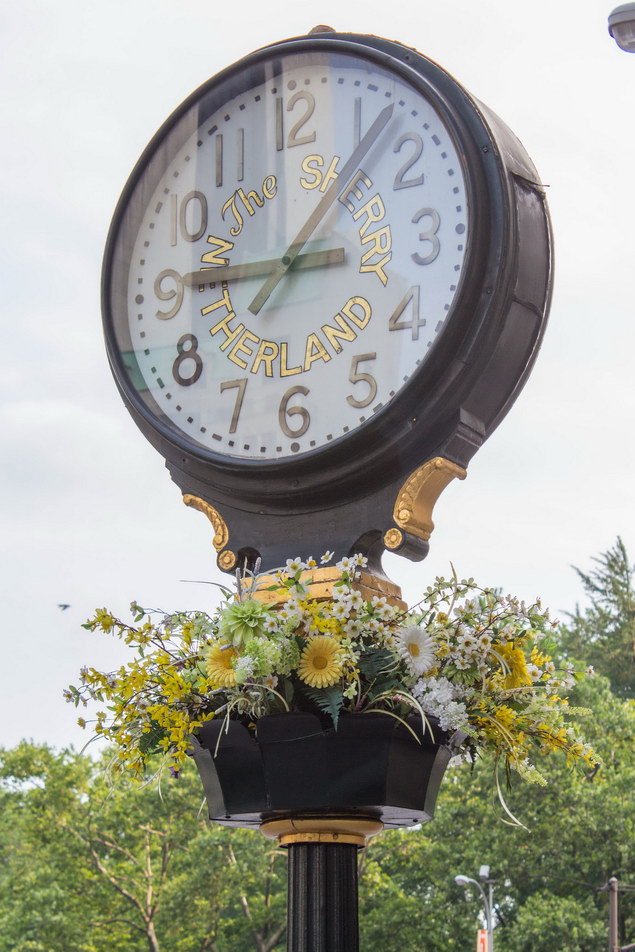
![[Sherry Netherland] IMG_3046 [6/11/2012 9:27:45 AM] [Sherry Netherland] IMG_3046 [6/11/2012 9:27:45 AM]](https://www.newyorkitecture.com/wp-content/gallery/sherry-netherland/IMG_3046_resize.jpg)
![[Sherry Netherland] IMG_3050 [6/11/2012 9:30:07 AM] [Sherry Netherland] IMG_3050 [6/11/2012 9:30:07 AM]](https://www.newyorkitecture.com/wp-content/gallery/sherry-netherland/IMG_3050_resize.jpg)
![[Sherry Netherland] IMG_4460 [6/21/2012 10:05:33 AM] [Sherry Netherland] IMG_4460 [6/21/2012 10:05:33 AM]](https://www.newyorkitecture.com/wp-content/gallery/sherry-netherland/IMG_4460_resize.jpg)
![[Sherry Netherland] IMG_4668 [7/3/2012 10:20:41 AM] [Sherry Netherland] IMG_4668 [7/3/2012 10:20:41 AM]](https://www.newyorkitecture.com/wp-content/gallery/sherry-netherland/IMG_4668_resize1.jpg)
![[Sherry Netherland] IMG_4791 [7/3/2012 11:34:29 AM] [Sherry Netherland] IMG_4791 [7/3/2012 11:34:29 AM]](https://www.newyorkitecture.com/wp-content/gallery/sherry-netherland/IMG_4791_resize.jpg)
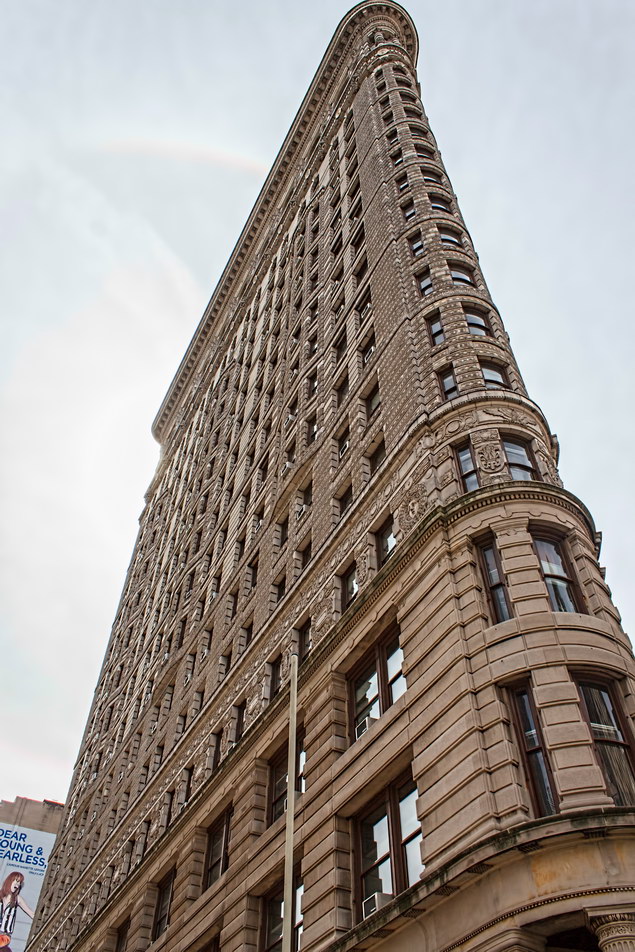
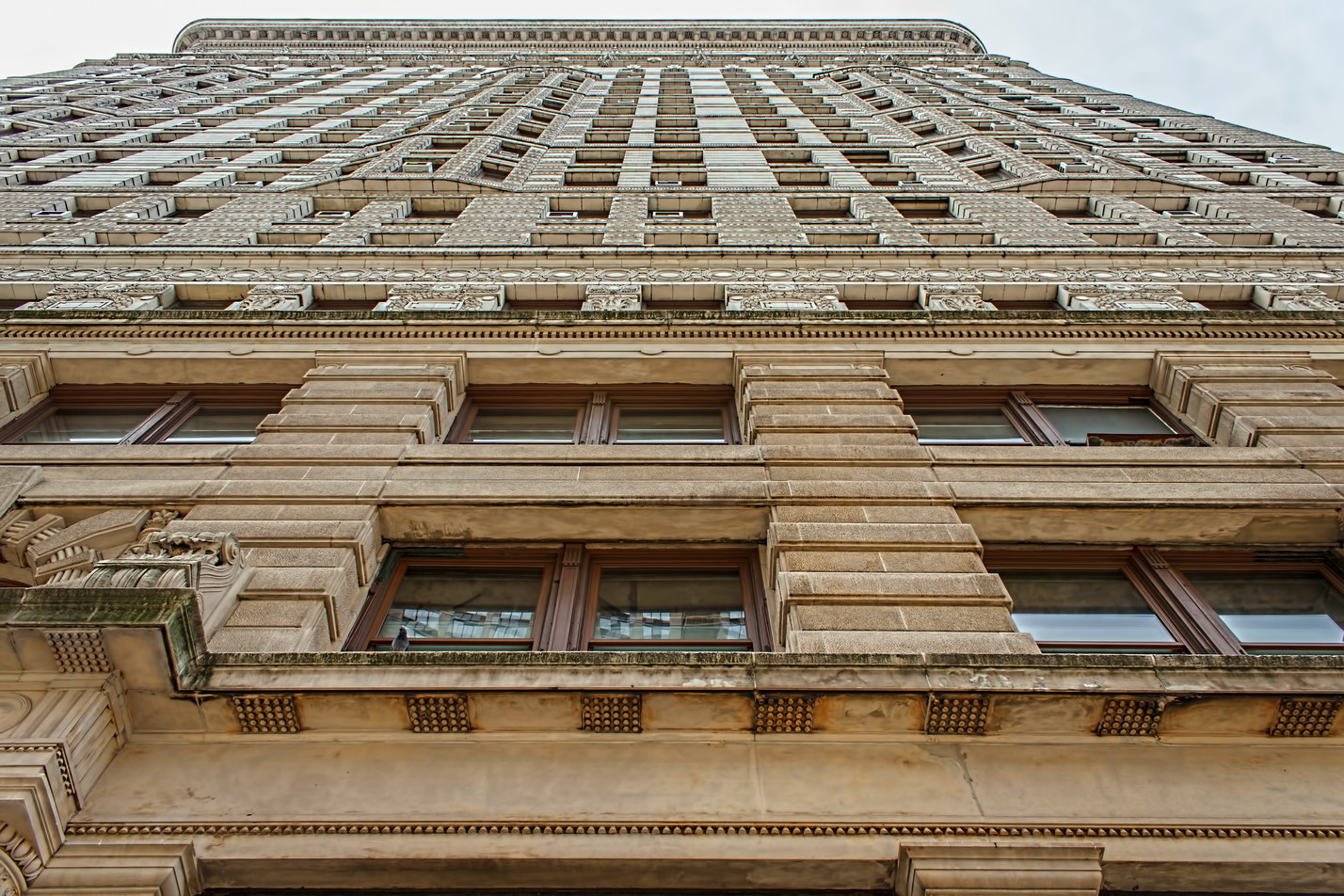
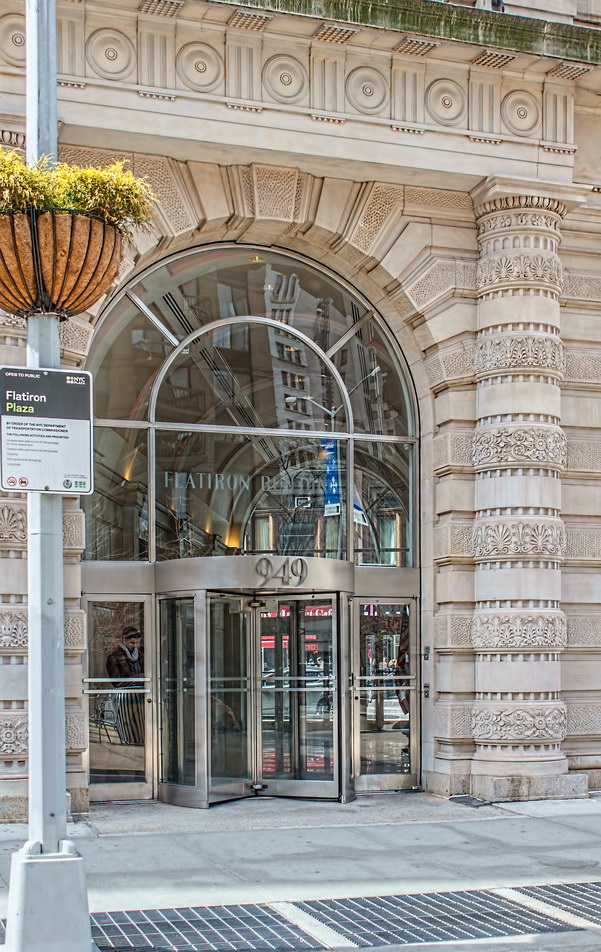
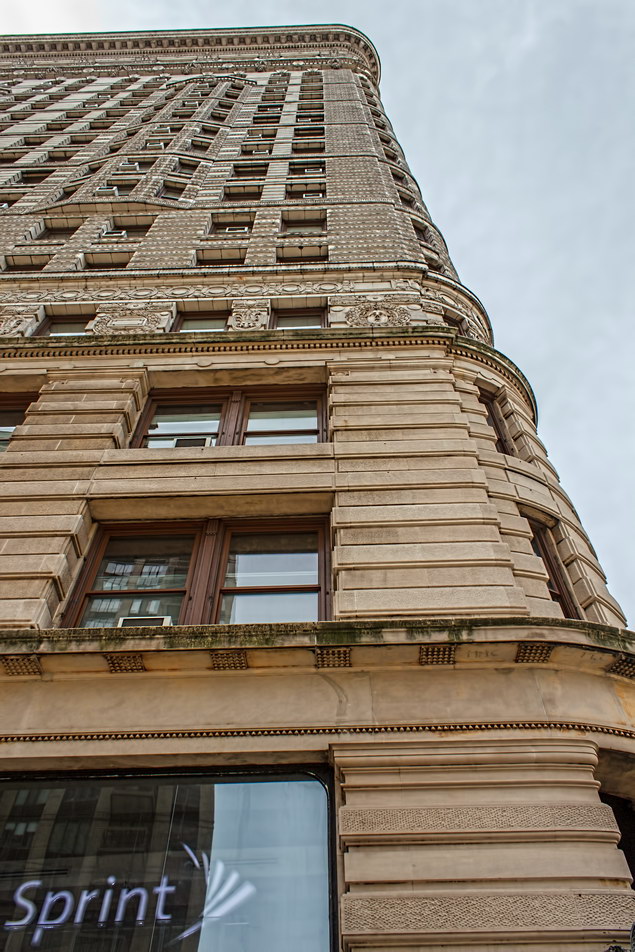
































![A_6065 [11/2/2011 10:14:27 AM] A_6065 [11/2/2011 10:14:27 AM]](https://www.newyorkitecture.com/wp-content/gallery/flatiron-building/A_6065.jpg)
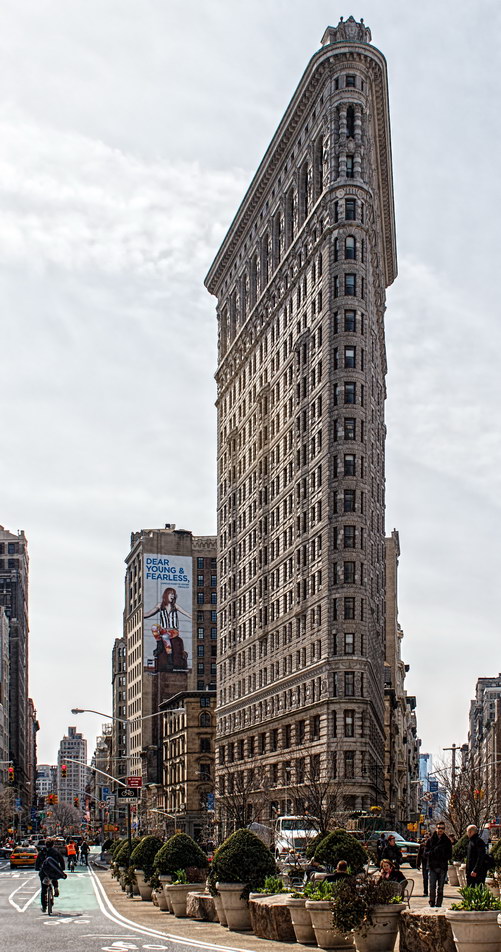
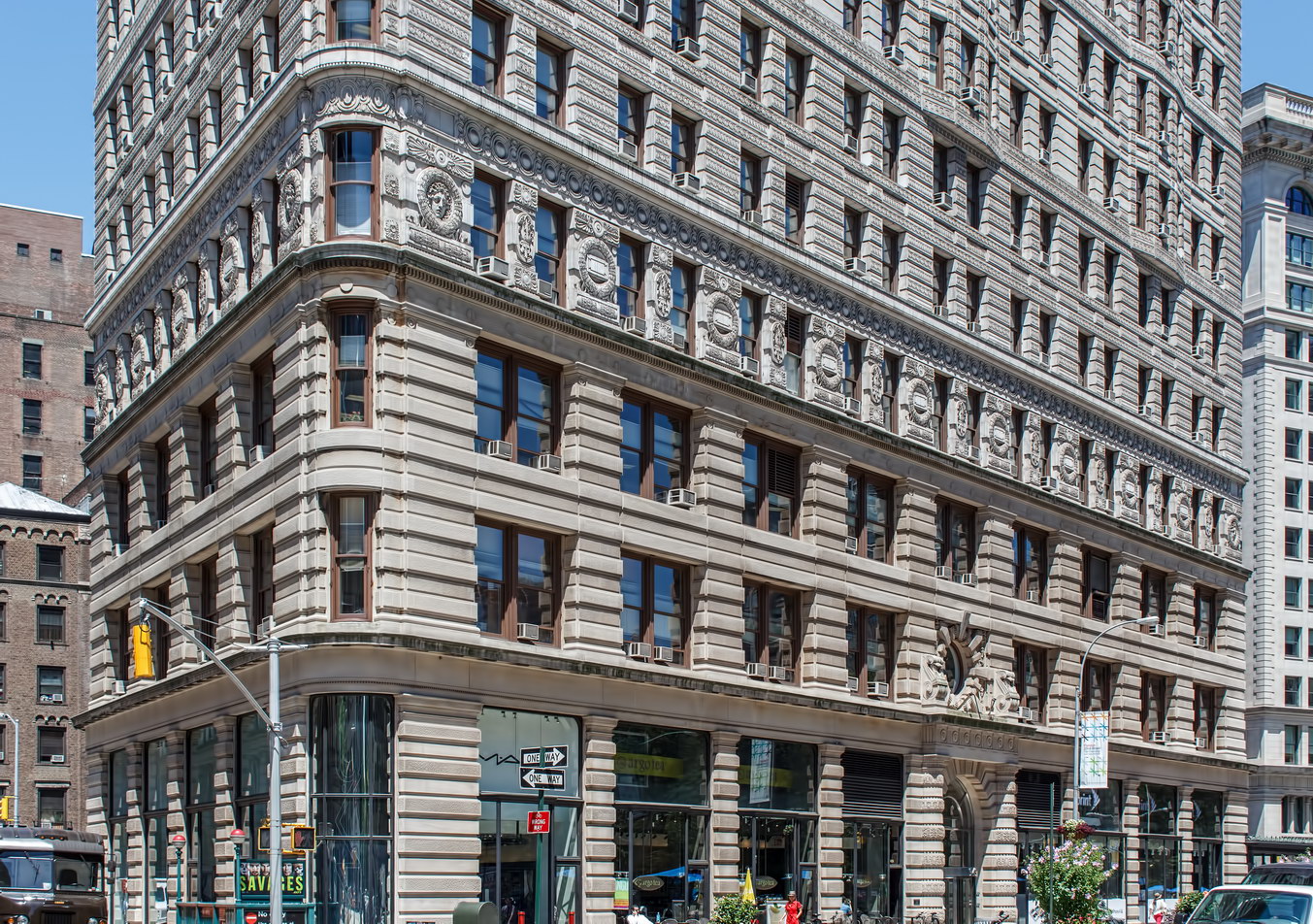













![IMG_4636_7_8 [3/12/2012 8:15:05 AM] IMG_4636_7_8 [3/12/2012 8:15:05 AM]](https://www.newyorkitecture.com/wp-content/gallery/flatiron-building/img_4636_7_8.jpg)











































